2026 Author: Priscilla Miln | miln@babymagazinclub.com. Last modified: 2025-01-22 17:55:13
Hamster is a cute pet. There are many advantages in its content, but many who want to buy this animal are often faced with the choice of which hamster is better to have: Syrian or Dzungarian? The fact is that these breeds are the most common in Russian homes. As representatives of the Khomyakov family, they are, of course, similar. But they also have several important differences that, when choosing a pet, may be decisive for the future owner.
How do the carriers of these two breed qualities differ from each other, and which hamster is better to buy: Syrian or Dzungarian, we will tell in this article.
First, let's define the description of these two types of decorative rodents.
Djungarian hamster. Appearance
This is a very tiny animal with a pointed muzzle and small ears. his little bodyweighs no more than 50 grams with a total length of no more than 10 cm. As a rule, it is covered with thick short fur, which in natural conditions is usually gray-brown in color with white patches. A blackish or dark gray stripe is pronounced along the line of the spine - this is a common species feature for dzhungaria. The belly, paws and the inside of the ears of the animal are usually white or light. Eyes - bulging, black.
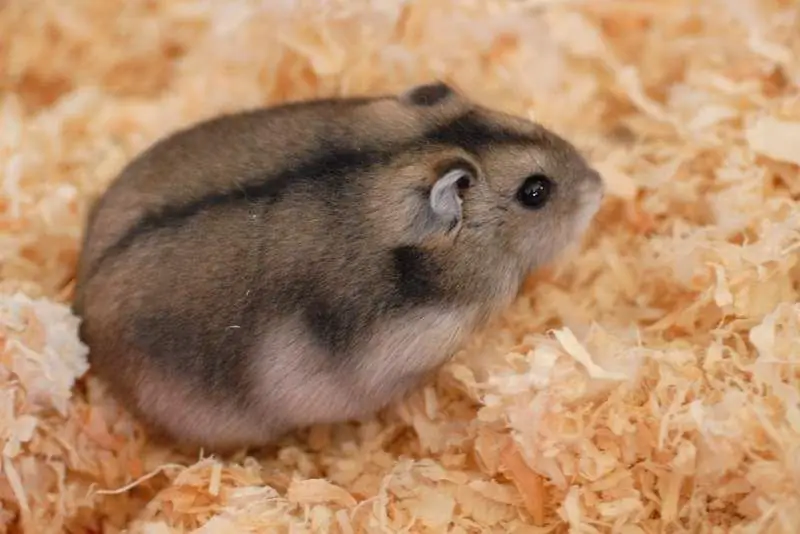

Domestic Djungarian hamster differs in color from wild. There is a common set of colors for domesticated animals: these are standard (gray-brown body with a white belly), sapphire coloring (bluish-gray, also with a light belly), pearl (whitish with gray flecks) and tangerine (cream with a red tinge).
But you need to take into account that individuals of this species molt in winter and become almost white - because of this, and also because of their small size, the jungar is sometimes called the Russian winter dwarf hamster. Nature provided for the hamster to be invisible in the snow, because the dzhungars do not hibernate and in winter conditions they also have to take care of food. True, it should be noted that in captivity, molting with a change in color is rare.
Where it lives in nature
Many people wonder where and how the Dzungarian (or Sungur) hamster lives in the wild. This interest is caused not just by curiosity: in fact, in order to provide the best living conditions for an animal in captivity, it is important to know what the lifestyle of its wild ancestors was.
In Russian open spaces, this type of hamster is very common, for example, inKhakassia, in some regions of Kazakhstan, in the steppes of Southwestern Siberia. For habitation, this rodent, due to food preferences, chooses semi-deserts and steppe spaces, where cereal herbaceous plants grow.
Djungarian hamsters are most active at night. They live in minks, which necessarily have several entrances and otnorok, as well as a nesting chamber.
The life expectancy of this rodent in the wild is small - no more than two, sometimes three years. At home, it usually increases, but only slightly.
Content Features
Although many owners do not listen to this opinion, jungars should not be placed several copies in one cage. However, experience in keeping this species in captivity has shown that it is best if there is only one animal in one cage.

The joint maintenance of a male and a female will lead to the appearance of offspring. If the animals are not further seated, their population will grow exponentially, and instinct will force the adults to eat their cubs. Usually this immediately causes quite understandable rejection from the owners, but here it should be understood that hamsters in their natural environment do not live in families, but single individuals in each area, and captivity conditions cannot change this. Therefore, if a female hamster has offspring, it should be separated after reaching a certain age (as soon as young hamsters are able to eat on their own).
Not recommended and the contents of twosame-sex hamsters together: in this case, aggression towards each other is possible, both in females and in males. In addition, living together in the same cage can cause a state of stress for each of the inhabitants, and this will inevitably affect their owners as soon as they try to communicate with them.
It is best to feed Djungarian hamsters in captivity with special feeds.
It is worth noting that pet stores often sell animals of hybrid origin under the guise of a Djungarian hamster. Such individuals may have an unstable psyche and a tendency to various diseases, including diabetes. A conscientious breeder will always provide you with a pedigree upon request.
And now let's look at materials about another, no less popular human companion animal.
Syrian hamster. Description
This representative of the Khomyakov family is larger than the Dzungarian - together with the tail (1.5 cm), the length of the body of this rodent is 13 (in rare cases, up to 18) centimeters. In this case, the weight can reach 120-125 grams. Representatives of this species, which are also called Golden hamsters, differ, respectively, in the golden or brownish color of thick soft fur. In the process of domestication and selection, the variability of coat color has expanded significantly: Syrian hamsters can be, in addition to the main ones, both black and silver-white, as well as bicolor and even tortoiseshell colors.
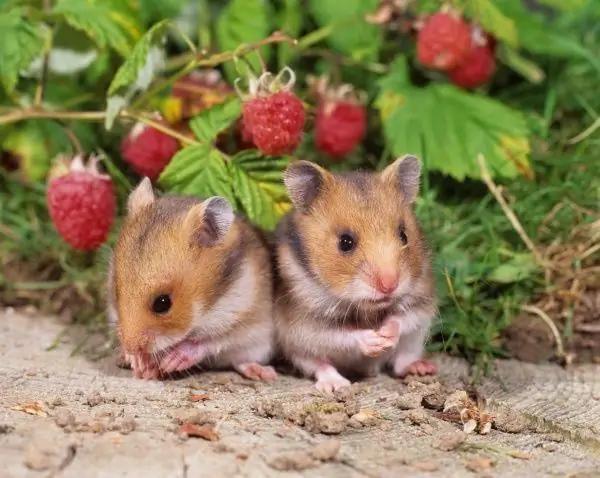

A feature that in animal science is assigned to allhamsters, but especially noticeable in Syrians, is the presence of cheek pouches. They are designed to transport food that the animal will get by exploring the surroundings to its mink. In addition, if there is a lot of food, this hamster is also inclined to store it in his bags. When full, the pouches hang from the cheeks to the very shoulders of the animal, which is why the name of this hamster is translated from Arabic as "Mr. saddlebags".
The rest of the features that can be distinguished when comparing the Syrian hamster and the Djungarian hamster are the protruding, noticeable ears of the former, a slightly more elongated muzzle, and the absence of a dark dorsal stripe.
Types of wool
Through the work of breeders, four separate subspecies of Syrian hamsters have been bred. These subspecies are distinguished by the following types of wool cover. The most common and common is the short-haired type. This plush-like fur looks best in different colors.
The long-haired Syrians are also bred, another name of which is Angorians. Males of this subspecies have a kind of "skirt" of long (from 8 to 10 cm) hair in the lower part of the body. However, the females look like ordinary Syrians, maybe a little more fluffy. In foreign pet stores, this variety is called "hamster - teddy bear" (Teddy Bear hamster).

Satin, or Satin Syrian hamster is distinguished by fur with a special, almost glossy sheen. They achieved this effect by breeding a new variety, in the fur of which there were hollow hairs. HoweverSatin Syrians should not be bred, as this may result in animals with sparse or no hair.
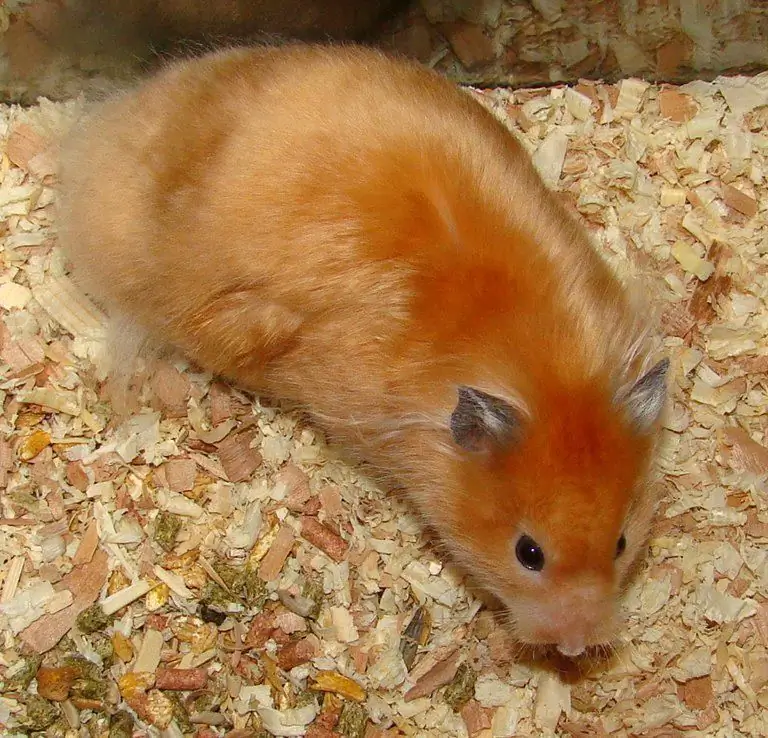

Rex (or Curly) hamsters give the impression of being disheveled animals - the hairs in their fluffy attire are slightly curled. In addition, Rexes also have twisted mustaches. This variety can be both short(-) and longhair type.

The last variety is represented by Hairless Syrian Hamsters. They are characterized by a complete lack of hair. However, animals with such a fixed mutation sometimes still have some velvety and even short "whiskers".
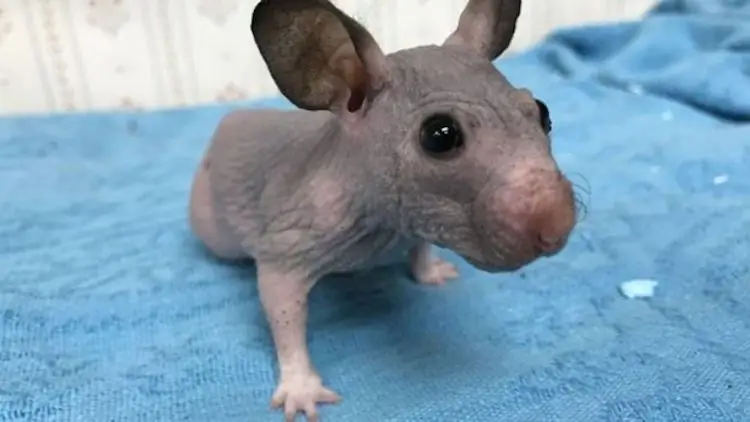
Unfortunately, representatives of the hairless Syrians are quite sickly, they require special care: in unfavorable temperature conditions, some owners even "dress" them. In addition, the life expectancy of a hairless Syrian hamster is half that of a normal one.
Where it lives and what it eats
Unlike the Djungarian hamster, the range of this animal is quite limited: it is found in the Syrian, Turkish and Israeli semi-deserts. Due to human activities, and because the species is considered a pest, the Syrian hamster's habitat is constantly declining, and according to the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN), this species is now listed as an endangered animal.
Like othershamsters, this one is most active at dusk or dawn. The Syrian is quite mobile: observations of zoologists have shown that during the "night shift" this animal is able to run from three to eight kilometers. Specifying which is better - the Djungarian or the Syrian hamster - keep in mind that the Syrian is more mobile, and often this activity manifests itself in the evening, when he begins to run around the wheel and master his home in every possible way.
The life expectancy of the Syrian hamster is short, it is the same as that of the jungars. This circumstance greatly upsets those who want to have this pet, who are thinking about which is better - a Syrian or Djungarian hamster.
The diet of the Syrian is much wider: this animal is considered a practical omnivorous rodent, because it is able to eat not only cereal seeds and all kinds of nuts (which, by the way, are forbidden to Djungarian hamsters), but also small insects. Of the nuts, however, almonds, as well as fruit pits, are contraindicated for Syrians.
Contents
Like the Djungarian hamster, the Syrian hamster is considered a territorially intolerant animal: cubs should be separated from their mother as soon as they are four weeks old. When the young animals reach eight weeks of age, in order to avoid skirmishes, they should also not be kept with each other.
Staying in their burrows, these hamsters act like active housewives, sorting and sorting out food supplies that have gone bad.
In order for the hamster to move more, it is worth installing a special wheel in the cage. Well, to everyonespecies of hamsters require wooden blocks or pieces of mineral stones to grind their teeth.
Which hamster is better to have - Dzungarian or Syrian?
Dzhungariki - hamsters with a calm character, they are easily tamed and even attached to their master and eventually can sit on a person's hand. However, this is only one of the opinions, there are other reviews of the owners who claim the same thing, but about Syrian hamsters. Therefore, most likely, the character of your future pet will be made up of various factors. In any case, the hamster must be purchased no older than a month or a little more, then it will be easier to tame it and help you get comfortable in a new place.
When answering the question which hamster is better: Dzungarian or Syrian, owners' feedback is something worth listening to. Despite the territorial intolerance common to hamsters, Dzungars still find it easier than Syrians (who are considered solitary animals) to settle down in a group with other hamsters. Of course, the wider the cage, the more skirmishes and fighting for territory between animals can be avoided. Therefore, a one-story cage is more suitable for the Dzungars, but the Syrians love to climb and they can be offered a compact high cage with tunnels and labyrinths.
Unlike the Syrian hamster, djungarians should be given low-sugar food. So, it is better not to offer persimmons, grapes and peaches.
Djungarian hamsters are active throughout the year, while Syrian hamsters are less mobile in winter, as their wild counterparts hibernate at this time.
Finally,according to some reviews, the smell in a cage with a Syrian hamster living there is more pronounced than from a jungarik, although with proper care this moment goes unnoticed.
We tried to answer a difficult question, what is the difference between a Syrian hamster and a Dzungarian hamster, and which one is better.
Recommended:
Which water tester to choose: an overview of models, their comparison and reviews

The problem of clean water exists in almost every home. Someone purchases and installs special filters, while someone just wants to check the condition of the liquid, so they buy a water tester. This device makes it possible to find out whether water is suitable for domestic use and whether treatment is necessary
Halogen or LED lamps: which is better, comparison, tips

Comparison of LED and halogen lamps is a hot topic for both motorists and ordinary consumers when choosing lamps for the home. In the last decade, these two artificial light sources have been actively competing with each other
Cooling teether - which one is better and how to choose? At what age should you buy a baby teether?

Teething causes a lot of discomfort to the child. The task of the mother in this difficult period is to relieve the pain and surround the baby with warmth and care. A cooling teether is one of the true helpers of a modern woman. On the shelves they are presented in various colors, shapes and sizes. But what should be guided by when choosing this device? Here you can learn how to choose a baby teether that will be safe for your baby
Which thermos keeps heat better? Which brand of thermos to choose?

Do you love frequent trips to nature? Are you a frequent participant in various hiking trips? Or your favorite hobby is fishing? If you answered yes to at least one question, then you know firsthand what the need to purchase such a device as a thermos is. The modern market offers a wide range of such products. But how to choose a high-quality thermos that keeps heat better from this multitude?
Cat tray. Which one is better and how to choose it?

In order to choose a tray for a cat, you need to know what they are. As well as the advantages and disadvantages of each variety. Then you can choose the right accessory

