2026 Author: Priscilla Miln | miln@babymagazinclub.com. Last modified: 2025-01-22 17:55:21
Mastocytoma is a neoplasm that affects the skin of an animal, which is formed by mast cells. Mastocytoma in dogs is a fairly common disease and accounts for 22-25% of all skin diseases. Most often, the disease affects a four-legged friend from the age of nine, but it can also appear at an earlier age.

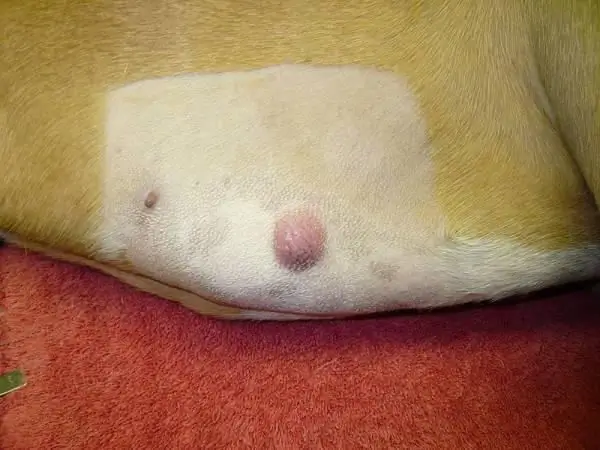
Mast cell tumor in dogs
It doesn't matter what sex the animal has: neoplasms can develop in both males and females. However, according to the observations of experts, some breeds are most often susceptible to the disease and constitute a risk group. These include Labradors, Boxers, Bulldogs, Boston Terriers, Setters, Pit Bulls, and Sharpeis, who suffer from the disease more often than others.
Mastocytoma in dogs is a mast cell tumor of the skin. If multiple clusters of such tumors are observed, then the disease is called mastocytosis. Tumors are formed from mutated mast cells.

Mast cells, or mast cells, are cells of the immune system that are involved in the formation of adaptive immunity and are found in connective tissues. They contain special granules consisting of heparin, histamine, interleukins and neutral proteases, which trigger defense mechanisms aimed at protecting the body from external and internal stimuli.
How and why the disease develops
Mast cells are located mainly under the skin near the lymph nodes and blood vessels. With constant exposure to negative factors, mast cells are modified and mastocytoma is formed in dogs, the causes of which are not fully understood.
Specialists believe that the cause of the disease is a mutation of the oncogene, which is involved in hematopoiesis and the growth of mast cells. Altering this gene can cause cancer.
How the tumor behaves depends on two factors:
- From local and systemic effects on the body of animals of vasoactive substances released from mastocytes.
- From the ability of tumors to metastasize and infect internal organs with cancer cells.
Local reaction to the released vasoactive substances may be different: edema, ulcers, erythema at the site of the neoplasm.
Systemic reactions include gastric ulcer, perforation of the walls of the stomach and intestines, resulting in peritonitis.
It is not uncommon for mastocytoma in dogs to develop systemically when mast cells proliferatein many internal organs: spleen, liver, bone marrow and others. In this case, the disease develops into mastocytosis.
Classification of mastocytoma
Mastocytomas can be of several types:
- Solitary single - characterized by slow growth.
- Solitary neoplasms metastasizing to lymph nodes.
- Multiple tumors.
- Mast cell leukemia or mastocytosis.
A feature of mastocytes is that they can occur both with severe symptoms and asymptomatically.

It is customary to distinguish between three stages of mast cell tumors in dogs:
- In the first degree, neoplasms are formed in the skin and are benign. They can be large and difficult to operate on, but there is no risk of spreading to other parts of the body.
- In the second stage, tumors form in the subcutaneous layer. There are some signs of malignancy here, and therefore it is not known how the cells will respond to treatment.
- In the third degree, deep subcutaneous areas are affected. Such a mastocytoma is quite aggressive and requires a special approach in treatment.
Appearance of a mastocytoma
Mastocytoma in dogs is often characterized as a mimic because it can take on a variety of forms and mimic any skin disease. Neoplasms can look like ordinary warts and like wet dermatitis, while identifying a dangerous disease is quite difficult, and sometimes impossible withoutspecial survey.
Symptoms of the disease
In half of the cases, a mast cell tumor affects the skin on the dog's body, but can occur on the head, neck and muzzle. Sometimes the disease manifests itself in the throat, digestive organs, or nose. Due to the fact that mast celloma is difficult to diagnose, veterinarians often make a false diagnosis and prescribe the wrong treatment. Any neoplasm must be carefully studied.
Most often, mastocytomas look like medium-sized nodules that cause itching. The dog begins to comb them and the formations turn red and inflamed. Hair loss is observed in the area of the tumor. When touching the tumor, the animal shows anxiety, because they are quite painful. Mastocytoma develops both rapidly and slowly.
How to diagnose a tumor
There are practically no specific manifestations that characterize neoplasms, but they can be easily diagnosed with a biopsy. A thin needle is used to take the material, so the dog practically does not feel pain. The seized materials are sent to the laboratory for a thorough study.
The cells that make up a mastocytoma are large and round. They contain substances that can cause vomiting, stomach ulcers, shock and death.

Mastocytoma cells are very unpredictable. Even today there is no one hundred percent ability to distinguish tumors that will proceed aggressively, recur, metastasize or lead to death fromcurable tumors.
Oncological diseases are fairly accurately diagnosed at the "Biocontrol" clinic. The veterinary clinic specializes in such diseases and has the necessary equipment.
In order to determine the prognosis of the disease, it is necessary to correctly identify the degree of differentiation of education, which will show how malignant cells are different from benign ones and what is the probability of a cure.
What the diagnosis is based on
For the correct diagnosis, a number of clinical tests are carried out, which give a detailed idea of the course of the disease. For example, the veterinary clinic "Biocontrol" on Kashirka carries out diagnostics:
- study of data on the course of the disease, examination of a pet, a comprehensive study;
- biochemical and complete blood count;
- abdominal ultrasound to detect or rule out metastases;
- X-ray of the thoracic region in bilateral and dorsoventral projections;
- aspiration biopsy of the composition of the lymph nodes that are the first to be infected;
- clinical bone marrow studies.
Vet clinic "Biocontrol" on Kashirka has been specializing in the treatment of dogs from oncology since 1965 and uses all known methods of treatment.
Mastocytoma treatment methods
When a disease such as mastocytoma is detected, treatment is prescribed using one of the methods:
- Surgical - removal of neoplasm. This method is used if it is possible to remove a mast cell tumor,while capturing 2-3 cm of he althy tissue located under the formation. It makes sense to remove a mastocytoma only in the first and second stages, because the disease can quickly spread to neighboring tissues. Before surgery, the dog is given antihistamine therapy to prevent anaphylactic shock and an allergic reaction.
- Radiation therapy method. It is carried out as the main and additional treatment. The result depends on the differentiation of cells and the size of the neoplasm. Radiation therapy is used if the tumor cannot be removed and the mastocytoma cells have a low level of differentiation. As an additional measure in complex treatment, irradiation is indicated before and after surgery for large formations.
- Chemotherapy method. It is used in the presence of malignant neoplasms with metastases to regional lymph nodes. The meaning of this method is the use of certain medications that block the development of cells with certain receptors. The presence of such receptors is determined by immunohistochemical analysis, by examining the composition of the tumor.

The results of any of the methods of treatment depend on the course of the disease and its stage. Thus, in the treatment of the first and second stages of the disease with an average or good degree of differentiation of tumor cells, the animal after treatment can live on average for more than two years. In the third and fourth stages and with a low degree of differentiation after treatment, the dog will live no more thansix months.
How a dog's mastocytoma responds to chemotherapy
In a typical chemotherapy regimen, "Prednisolone" is prescribed, the dosage of which is calculated depending on the weight of the animal. After two weeks of taking the drug, the results are checked. And if no positive effect is detected, then the next chemotherapy protocol is prescribed, which consists of Cyclophosphamide, Vinblastine and Prednisolone.
"Prednisolone" is most often used for mastocytomas. Animals tolerate it well and the duration of administration can last six months. If no new tumors are found during treatment, the drug may be discontinued.
When taking the drug, body weight may increase, appetite and thirst may increase, skin infections and shortness of breath may occur. Less common are indigestion, peptic ulcers, and pancreatitis. If such symptoms occur, then additional therapy is prescribed to reduce side effects.

If the tumor is located in hard-to-reach places or it cannot be removed, then combined chemotherapy is used. It inhibits the growth of the tumor and its spread throughout the body for a long time, which can be calculated in weeks, months and years. Complete elimination of a mast cell tumor is not possible, but some animals may live a few more years and reach biological old age.
Observation aftertherapy
All animals treated for mastocytoma should be under the constant supervision of veterinary oncologists. For example, "Biocontrol", a veterinary clinic that specializes in the treatment of oncology, monitors each patient.
In case of early detection and timely treatment of a recurrent tumor, the chances of prolonging the life of the animal increase. Usually, the examination of the dog is carried out at intervals of one and a half to two months after the surgical removal of the mastocytoma and every three weeks in the case of chemotherapy. Periodically, specialists will take the necessary tests.
What are the predictions?
Despite the fact that with a disease such as mastocytoma in dogs, the prognosis is difficult, there are still some signs that can show a positive trend in the disease. The behavior of a mastocytoma is affected by the classification and stage of the tumor, as well as the age of the dog. Much also depends on immunohistochemical studies, which determine the number of altered cells and the effectiveness of therapy.

So, with a highly differentiated mastocytoma, an animal can live long enough, with a moderately differentiated mastocytoma, life expectancy ranges from one year to three years, and with a poorly differentiated one, from 6 to 12 months.
Factors affecting tumor behavior
- Degree of differentiation.
- The stage at which the tumor was detected.
- Location of neoplasm. The worst prognosis is given for tumors located in the mouth and onmucous membrane.
- The size of the tumor. The larger the mastocytoma, the less chance of a favorable outcome.
- Intensity of development. With the rapid growth of a neoplasm and damage to neighboring tissues, the chances of recovery are sharply reduced.
- Symptoms of damage to the digestive system indicate the neglect of the disease.
- Age group of animals. The older the pet, the more difficult the treatment.
- Gender of the dog. Studies show that males tolerate chemotherapy worse than females.
- Breed of animal. In some, mastocytoma can be diagnosed in the early stages, for example, in boxers. In others, the disease manifests itself only in a neglected state. Sharpei are a striking example.
Prevention measures
Unfortunately, there is no way to prevent the formation of a mast cell tumor. The only recommendation for owners of dogs, especially those belonging to the risk group, is the constant monitoring of the skin of a four-legged friend, checking for the presence of various seals. It will also be useful to regularly take tests and visit specialists.
Mastocytoma is a rather serious and complex problem both in terms of diagnosis and treatment. The disease requires a qualitative study. What is a mastocytoma in a dog, whether to operate or not, how to treat and whether it is possible to cure - such questions swarm in the head of every good owner. It all depends on the stage at which the disease was detected, and on the results of the preliminary examination. With a favorable outcome of treatment, the four-legged friendhas every chance of a fairly long life (by dog standards).
Recommended:
Cirrhosis of the liver in dogs: symptoms and treatment, life prognosis

It would seem that cirrhosis of the liver is a completely human disease that occurs most often with the abuse of alcohol and fatty junk food. But our smaller brothers - cats and dogs - also suffer from this disease. So, cirrhosis of the liver in dogs, symptoms and treatment, as well as diagnosis and causes of occurrence - we will consider all this in this article
Peritonitis in dogs: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, prognosis

The inflammatory process that occurs in the peritoneum of a dog has received the medical name "peritonitis in dogs." Pathology is most often transmitted from the affected internal organs. The disease is quite serious, threatens the pet's he alth with severe complications and even death. Breeders mark the body temperature of a pet, reaching the limit marks. Also, the animal may experience pain shock, due to which it loses consciousness
Symptoms of parvovirus enteritis in dogs and cats. Treatment of the disease

You have a puppy at home. Of course, this is a joyful event, but you must remember that it is also a huge responsibility. First of all, you must monitor the he alth of your pet and try to protect him from the most serious diseases, in particular from parvovirus enteritis
Ferrets: diseases, possible causes, symptoms of the disease, treatment, prevention and advice from veterinarians

Recently, more and more often, fans of pets give birth to ferrets in houses and apartments. Animals are undemanding in content, mobile, intelligent and cheerful. And yet there are some nuances that you need to know if you are going to make such a friend. Despite strong immunity, there are a number of ferret diseases that attentive owners should be aware of
Mammary tumor in cats: symptoms, treatment, prognosis

Cancer in animals, particularly mammary tumors in cats, is common. This disease claims the lives of four-legged pets that are unable to resist the disease