2026 Author: Priscilla Miln | miln@babymagazinclub.com. Last modified: 2025-01-22 17:55:15
When childbirth approaches, a woman, although she is looking forward to this moment, really wants to carry the baby to the right time. Unfortunately, in the later stages, when, it would seem, all pregnancy tests have been passed, complications can arise. One of them is placental abruption. To understand what it is and what threatens the mother and baby, you need to figure out what the placenta is.
Organ and its functions
The placenta is a completely unique organ. First, it exists temporarily - only during pregnancy. Secondly, the placenta is considered the organ of the fetus, but it can be considered that it belongs to two at once - the baby and the mother. This is exactly where the blood of the mother and fetus meet, but they do not mix due to the placental barrier. The placenta primarily performs nutritional and respiratory functions. Through it, the baby receives the necessary water, vitamins, minerals, glucose, and oxygen. Carbon dioxide and waste products of his rapidly growing organism are removed from his body. Besides, sheprovides immune protection to the fetus. Maternal antibodies pass through the placenta. But the work of the placenta is important not only for the child, but also for the body of the woman herself. It produces hormones that help regulate pregnancy properly, as well as prepare the mammary glands for the upcoming feeding. Dr. Michel Auden called the placenta the baby's advocate. While, for example, the roots of a plant absorb those substances that are in the soil, the placenta can partly "control" the process, extracting everything necessary from the mother's blood. Providing the baby with nutrients and oxygen is so important that the placenta can even come into conflict with the mother's body. People say that the child will take his own.
True, do not overestimate the capabilities of this body. Otherwise, there would be no underweight children, babies with developmental delays or those affected by a deficiency of any necessary substances. In addition, the placenta cannot protect the child from the effects of alcohol, nicotine, drugs and viruses. Therefore, pregnant women are advised to lead a he althy lifestyle and beware of colds and infections.

Structure of the placenta
The placenta has the shape of a disk with a diameter of about fifteen to twenty centimeters and a maximum thickness of 2.5 to 3 cm, it is somewhat narrowed towards the edges. By the way, the name of the organ comes from the Latin placenta - flat cake, cake. In the cuisine of some peoples, such as Moldovans, there are pies pies that have a round flat shape. Their name is also related to the Latin word.
Placentaattached to the wall of the uterus. Its formation begins already on the seventh day, when the membranes of the embryo are formed - the chorion and amnion. The chorion is transformed into the placenta, which at week 12 looks like a round cake with thinned edges, and at week 16 it is already formed. Thus, this organ overtakes the formation of the fetus in its development.
The umbilical cord departs from the placenta, in which there are normally three vessels. Interestingly, arteries and veins change roles here. Arterial blood, rich in oxygen, enters the child's body through the umbilical vein. Carbon dioxide and waste products leave his body through two umbilical arteries. These arteries are coiled around a thicker vein.
The placenta consists of lobules densely permeated with small vessels. The maternal vascular system is connected with the vessels of the uterus, on the side of the fetus it is separated from it by the amnion, so the blood of the mother and child only exchanges substances, but does not mix. After the birth of a child, doctors always examine the afterbirth that has left the mother's body. The two sides of the placenta look different. From the side of the fetus it is covered with a smooth, slightly grayish shell, and the maternal one has a pronounced structure of the lobules.

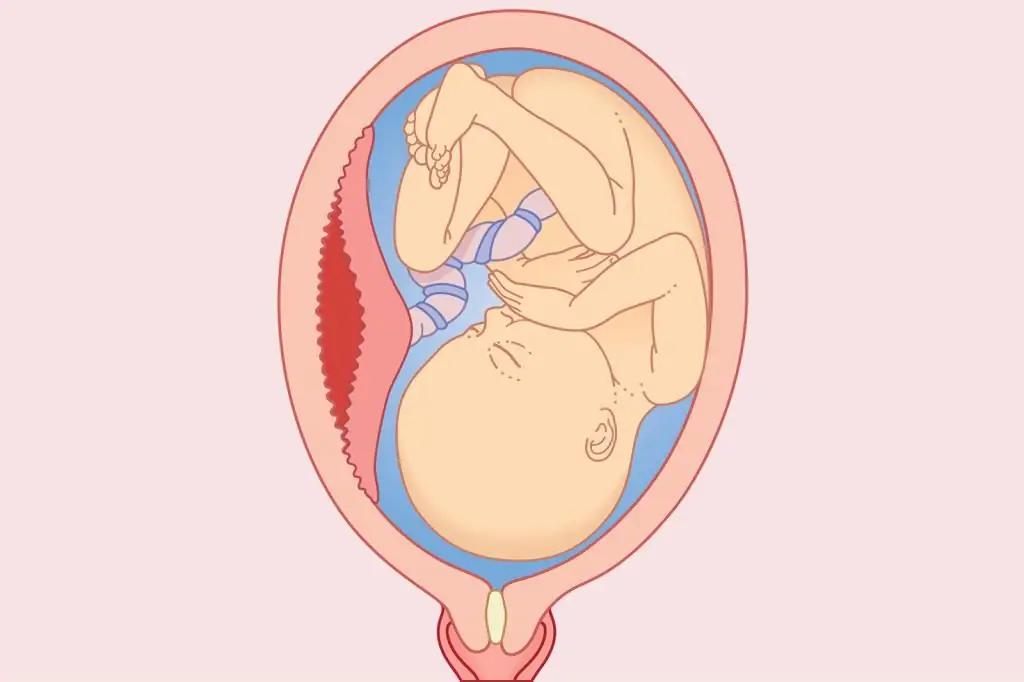
Placental abruption
This pathology is a separation of the organ from the mucous membrane of the uterus, complete or partial. In the resulting narrow cavity, blood accumulates, which even more pushes the placenta away from the uterine wall. All this is normal in the third birth period, when the afterbirth should come out, but it is dangerous duringpregnancy.
Placental abruption at different stages of pregnancy
The risk of the consequences of this phenomenon depends on the duration of pregnancy. In the first trimester, with timely diagnosis and treatment, it may not harm the mother and baby. After all, the placenta is still growing and developing, so its increase in area and volume compensates for damage.
The second trimester is characterized by high muscle tone and tension. Treatment depends on the specific situation and timing. For example, at the beginning of the second trimester, compensation due to the growth of the placenta is quite possible.
In the third trimester, late in pregnancy, the consequences of placental abruption are most serious. This organ has already ceased to grow, so the loss of substances coming to the child with blood is no longer replenished. And yet, depending on the amount of damage, there are two outcomes of events. In some cases, it is impossible to do without delivery, especially for a premature baby at such a time it is already possible to go out. Under more successful circumstances, a woman can bring the child to term, however, she will have to go to the hospital for preservation. This happens if the area of detachment is relatively small, there is no bleeding and the process does not progress.
Finally, placental abruption can occur during labor, but several hours ahead of time. While normally this should happen only in the third stage, sometimes it happens in the first or second - during contractions or attempts. In this case, doctors may prescribe a caesarean section or induce labor. After all, even at the time of birth to the baby through the umbilical cordthe necessary substances are still supplied, primarily oxygen, and he may suffer from hypoxia. In addition, bleeding can be dangerous for the mother.

Causes of placental abruption
Why does placental abruption occur in the later stages? There is no single answer to this question.
Disturbances in the vascular system can make the capillaries fragile, this can severely impair blood flow and provoke bleeding. This can be observed with preeclampsia, as well as with diseases not associated with pregnancy - diseases of the cardiovascular system, kidneys, obesity, diabetes.
Another cause of placental abruption in late pregnancy can be degenerative or inflammatory processes in the uterus and baby's place. This happens, for example, with uterine fibroids or overgestation, when the placenta is aging, and the baby has not yet been born.
This disorder can be caused by toxins that enter the body with bad habits - drinking alcohol, smoking, drug addiction. However, during pregnancy it is important in any case to give up bad habits. They entail a huge number of consequences and become the causes of placental abruption in the later stages. Moreover, an unhe althy lifestyle can harm much earlier, causing pathologies in the fetus - from prematurity to mental retardation. Only the use of alcohol is questionable: some sources advise categorically to refuse alcoholic beverages and alcohol-containing drugs, others allow the use of red wine in very small doses. But everythingit's better to be safe. Living 9 months without wine, which you still can’t drink a lot, is quite real, and the child’s he alth is worth it!
Anemia is also conducive to pathological processes. True, it should be understood that a slight decrease in hemoglobin is permissible during pregnancy. After all, the amount of fluid in the mother’s body increases greatly, so the blood can become “diluted.”
More often, placental abruption occurs with repeated births, which is associated with changes in the uterine mucosa. The risk of it increases with multiple pregnancies.
It is also provoked by autoimmune diseases and allergies, especially to donated blood and protein solutions. It can also be a dangerous side effect of certain medications.
Of course, mechanical damage in case of abdominal trauma can also affect, which can happen during a fall, household injury, accident.
Also, there are such causes of placental abruption in the later stages as heavy physical exertion and emotional stress. Therefore, pregnant women are advised to take care of themselves, and their relatives to help expectant mothers in everyday life and avoid conflicts.
In the presence of any harmful factors, it is important to regularly see a doctor, follow his instructions and be attentive to your he alth.
All of these reasons are specific to different stages of pregnancy.

Symptoms
The three main signs of placental abruption in late pregnancy, as well as in earlier ones, are bleeding, tension and pain in the uterus andfetal heart failure.
Bleeding depends on how the placenta detached. If its edge has separated from the wall of the uterus, the bleeding will be external, visible. In this case, brownish discharge from the vagina will become a symptom of placental abruption in the later stages. If a pregnant woman finds such discharge in herself, you should not consult a doctor. This happens in most cases of placental abruption in late pregnancy, but there are also internal bleeding. If the middle of the placenta is separated, and the edges remain in place, the blood accumulates inside in the form of a hematoma, and there is no discharge. This option occurs in 20% of cases. True, in this situation, placental abruption in the later stages will not remain completely invisible. The pain that is characteristic of this pathology is stronger with internal bleeding. It may be accompanied by general malaise - weakness, nausea, dizziness. Such symptoms can be observed with any bleeding in the body. The uterus is tense, when feeling the woman feels pain. These signs of placental abruption in the later stages may be of a different nature. The pain may be dull or paroxysmal. It may not be felt in the abdomen, but may be given to the thigh and perineum.

Heartbeat and movement
Obstetricians-gynecologists do not accidentally listen to the baby's heart rate at every examination. Violation of the cardiac activity of the fetus can be evidence of many different pathologies of pregnancy, including placental abruption in the later stages. The severity of sufferingfetus depends on the area of the separated placenta and the amount of maternal blood lost. If 1/4 of the placenta has moved away from the wall, disturbances in the functioning of the baby's heart become noticeable, but if 1/3 - the fetus experiences severe oxygen deficiency. After all, the placenta carries the child not only nutrients, but also oxygen, and its lack is reflected in the work of the body very quickly. Detachment of half of the placenta can be fatal for the fetus.
From the movement of the fetus, we can assume what is happening to him. With a slight lack of oxygen, the baby begins to move very actively. With these movements, he massages the placenta and stimulates the flow of oxygen-rich blood. If the situation worsens, and hypoxia intensifies, the fetus calms down - it simply does not have enough strength to move. A particularly alarming sign is the lack of movement during the day. After 30 weeks, it is highly likely to be a symptom of placental abruption in late pregnancy.
Diagnosis
If there are suspicious signs, such as bleeding, pain and discomfort in the abdomen, increased tone, changes in the movements of the child, conduct additional studies. In such cases, ultrasound is mandatory. This method allows you to learn a lot about the condition of the fetus, uterus and placenta. Several signs are evaluated during the procedure. Fetal heartbeats are counted. The thickness of the placenta is measured, the presence of changes in its structure is assessed. In the presence of a hematoma - a dangerous symptom of placental abruption in the later stages, its dimensions are measured.
After 34 weeks everyonepregnant women do cardiotocography (CTG). It also allows you to measure the fetal heart rate and rhythm. In addition, the condition of the muscular layer of the uterus is assessed. Its increase means readiness for premature birth.

Treatment of placental abruption
If there are several weeks left before the birth, it is better to speed up the birth than to wait for the unpleasant consequences of placental abruption. In later terms, early birth is not so scary.
But in favorable cases, the expectant mother can be admitted to a hospital. At the same time, strict bed rest is observed. The patient is under day and night medical supervision. The child's condition is regularly monitored using dopplerography and cardiotocography. Any deviation may be an indication for an emergency caesarean section.
Women who had a placental abruption in a previous pregnancy are referred to the hospital from 36 weeks, even if no dangerous symptoms are observed.

Real people experience
What do women write about placental abruption in the later stages? Reviews about this pathology are very different. Unfortunately, a significant number of pregnant women have lost their babies. Such women lament that the pathology was discovered too late or not detected at all. Detachment of the placenta also threatens the life of the mother - severe bleeding during childbirth is very likely. However, modern medicine allows almost all women to survive. So don't focus on the negative. Positiveemotions, even when pathology is detected, can help to carry the baby safely.
Always remember that many children have been saved by cesarean section. Moreover, pregnancy with placental abruption in the later stages and cesarean section is not a sentence. Many women with this pathology became pregnant again and gave birth to he althy children without complications. There are also cases when childbirth with placental abruption took place on time. So never lose faith in the best. With a careful attitude to your condition, you can avoid very many dangerous consequences. And if you consult a doctor in time and regularly undergo examinations for pregnant women, you can minimize the risk of pathology.
Recommended:
Placental abruption in early pregnancy: causes, symptoms, treatment, consequences
The modern rhythm of life and an abundance of stress often cause placental abruption in early pregnancy. With such a pathology, many women lie in conservation. During the first trimester, any negative impact on the physical or moral state of the mother can be fatal. But if you notice a deviation in time, there is every chance to avoid losing a child
Constipation during late pregnancy: causes, treatments, tips and reviews

What does constipation mean during late pregnancy. The main causes and characteristic symptoms. Effective methods of treatment and practical recommendations. The use of folk remedies, proper nutrition. Use of drugs
Nausea in late pregnancy: causes, possible consequences, treatment, reviews

At the beginning of pregnancy, a woman's nausea is considered the norm, but in the last period of bearing a baby, late preeclampsia (toxicosis) usually requires immediate treatment. The fact is that this condition occurs due to pathological changes in the nervous and cardiovascular systems, as well as the kidneys. Undoubtedly, this can be dangerous for the he alth of both the child and the expectant mother. Causes of nausea in late pregnancy include:
Heartburn during late pregnancy. Remedies for heartburn during early and late pregnancy

Heartburn during late pregnancy is extremely common. It affects about 85% of pregnant women. To alleviate the condition, it is important to know the factors that provoke a burning sensation in the esophagus
Diarrhea during late pregnancy: causes, treatment, consequences

Every mother-to-be should follow a diet, regardless of her he alth condition. But if a pregnant woman has diarrhea, then the diet should be observed especially strictly. The main purpose of such nutrition is to simplify the work of the body, regulate the work of the gastrointestinal tract, and exclude products that have laxative properties. But with such nutrition, the necessary amount of nutrients should be supplied to the body of a pregnant woman

