2026 Author: Priscilla Miln | miln@babymagazinclub.com. Last modified: 2025-01-22 17:55:16
Sooner or later, young parents are faced with the question of when and how to start introducing complementary foods into the baby's diet. As the child grows and develops, he becomes more and more active, and breast milk gradually loses the ability to fully replenish the supply of vitamins, minerals and trace elements necessary for a growing body.
Quite naturally, there is a need to switch to food that has a higher energy value and concentration of nutrients compared to mother's milk or adapted formula. In the article, we will consider how to properly introduce complementary foods for months while breastfeeding.
What is the difference from supplementary feeding?
To understand the difference, you need to define the meaning of each of these concepts.

Complementary foods are the introduction of a new (thick) food into the diet of an infant, with the exception of formula milk and milk, more variedand concentrated. Such food includes: puree from vegetables and fruits, yolk, cottage cheese, meat and fish puree, milk porridge, kefir. With artificial, as well as with breastfeeding, complementary foods are introduced for months according to the scheme.
Supplementary feeding is an addition to the main food for a child of the first year of life with a lack of mother's milk. As an additive, as a rule, dry mixes or products of plant origin are used. Supplementation is given to the child one or more times a day as a separate meal, alternating with breastfeeding, or combined with application in one feeding.
Complementary feeding rules if the baby is breastfed
Despite the value of women's milk, as the child grows, it is necessary to expand his diet, preparing for adult food and saturating the growing body with nutrients and vitamins. Moreover, the timely introduction of complementary foods develops chewing functions, stimulates intestinal motility, and promotes digestion.
The following guidelines must be followed:
- Any new product is allowed to be introduced only when the child is he althy.
- You should not start feeding your baby in hot weather or during the period of preventive vaccinations.
- Adhere to the principle of non-violent but forceful introduction of new food. Most babies refuse to take their first complementary foods while breastfeeding. Sometimes this process is delayed for more than one week, the baby continues to spit out the product again and again. It is important to be patient here.
- A new taste of the product should be introduced no earlier than three weeks after the absorption of the first.
- Complementary foods are allowed to be given before or after breastfeeding, but certainly from a spoon, not through a nipple. Most world-famous pediatricians say that it is better to give it before the main meal, when the baby is hungry. So more likely to teach him. However, if the baby is more willing to eat after breastfeeding, you can complement them later.
- Begins breastfeeding complementary foods at 6 months.
- Each product introduced into the baby's diet, they begin to give a few drops, gradually increasing the portion to the desired volume, carefully monitoring individual tolerance.
- The new product is introduced in the morning to be able to observe the reaction of the child's body. In the case when negative manifestations are observed in the form of colic, rashes and other reactions, the product should be excluded from the crumb menu for an indefinite period. If, upon repeated administration, the body responds with a similar reaction, the product is replaced with a similar one.
- Complementary foods are introduced, starting with one-component products, eventually moving to two-component products from the same group. This is done to prepare the child's digestive system and identify a product that can cause allergies. Then in the future it is not combined with other ingredients.
- The consistency of the food offered to the child should be homogeneous and not cause difficulty in swallowing. Coarse food is gradually introduced into complementary foods by 12 months.
- Meals for the baby should be warm or roomtemperature, hot and cold food are excluded. Before feeding, the dishes are cooled or, conversely, warmed in a water bath at a water temperature of +50 °C or in a baby food heater up to +37 °C.
- Complementary foods for babies should mainly be based on industrial products, which are produced under the strictest quality control. Regardless of seasonality, the composition of such jars is optimally balanced with vitamins and minerals. When buying, pay attention to the release date. If the dishes are made independently, vegetables and fruits should be fresh, seasonal, not imported. During the cooking process, hygiene is observed, spices, seasonings and other additives are not added to food.
Complementary feeding rules if the baby is artificial
If, for some reason, the baby is fed formula milk, then formula-fed complementary foods are introduced a little earlier than breastfeeding.

The main recommendations are:
- Check with your doctor before starting supplementation.
- The introduction of complementary foods does not mean that the child is transferred to adult food. He is still supplemented with adapted formula.
- Artificial babies are introduced to complementary foods from 4 months. In some cases even at three months of age.
- New food is introduced to a perfectly he althy child. If he is teething, he is stressed (due to moving, separation from his mother, etc.), the process should be postponed.
- Begin feedingwith applesauce or juice. Artificials start to give fruits, and then vegetables, breast-fed - on the contrary.
- First serving is 5-10g, daily dosage is increased by 10g until the norm is reached.
- If the baby does not like a certain taste, it should be excluded for a while and try again in 2-3 weeks.
- If the child is full, do not force him to finish eating the entire portion.
- Before introducing a new dish, you need to take a break for a week to determine the body's reaction to the previous ingredient.
- When allergy symptoms are detected, the product is excluded from the child's diet. You can enter it again no earlier than in a couple of months and under the supervision of a specialist.
- Meals can be cooked by yourself and given only fresh. Do not feed your baby food that has been cooked for more than 24 hours with spices, s alt, or sugar added.
- Food for the baby should be heat treated, be liquid. When the child grows up (closer to a year), they gradually introduce complementary foods of a thick consistency.
- When buying ready-made meals, it is important to take into account the age of the child, pay attention to the integrity of the container, the composition and expiration date of the product.
- If the baby flatly refuses complementary foods, you can add a little mixture to it for taste. Vegetable or butter is added to the food of older children.
- Complementary foods are best given on an empty stomach and then, if necessary, supplement the baby with formula.
- The dosage of a serving is calculated based on the needs of the baby, hisage, weight and developmental characteristics.
Types of complementary foods
This is a food that is introduced into the diet of a child in the first year of life as an addition to breastfeeding or artificial feeding. It is made from products of animal or vegetable origin, depending on the age and physiology of the child. Among them:
- Complementary foods on a milk-grain or grain basis. Made from flour of various types of cereals - this is a free-flowing dairy-free or milk porridge, baby cookies.
- Plant based complementary foods. Food made from fruits, berries or vegetables may be offered as canned juices, nectars, purees.
- Complementary foods based on meat. It is a food made from lean lamb and pork, veal, chicken, horse meat, rabbit meat, turkey.
- Milk-based complementary foods. Liquid, free-flowing, pasty food made from cow's or goat's milk. Dairy products - kefir, fermented baked milk, cottage cheese, yogurt.
- Complementary food based on fish. Dishes made from sea, ocean or freshwater fish.
Scheme
Today, experts offer several complementary feeding schemes, however, none of them is mandatory. Products should be selected based on the characteristics of the he alth and development of the child (underweight, food allergies, diarrhea, impaired digestion, etc.). Before introducing the first complementary foods while breastfeeding or formula-feeding, you should consult with a specialist. The pediatrician will tell you about what product it costsstart, and is the child ready.

Indicative charts:
- Start - vegetable complementary foods (zucchini, cabbage, potatoes, carrots, beets, etc.). This is the most optimal option for introducing food other than milk into the diet. It is suitable for premature babies who are anemic, rickets, constipated, overweight or underweight.
- Start feeding with porridge. This option is more suitable for babies who are not gaining weight well due to lack of nutrition or unstable stools, possibly due to the introduction of vegetable puree into the diet. In such cases, it is better to start with cereals.
- Complementary foods according to the method of Dr. Komarovsky. This nutrition scheme was developed by a notorious pediatrician and is based on his own opinion. Komarovsky suggests introducing kefir into the diet of a six-month-old baby. However, according to many experts, it should not be given to the baby until he reaches the age of eight months.
- Start complementary foods with fruit puree or juice. A regimen that starts with minimal servings of fruit puree or juice has been recommended by pediatricians for decades and is still used by moms all over the world. At the same time, citrus fruits should not be on the menu.
To determine which first complementary foods should be given to the baby, you need to analyze his condition, consult with a pediatrician.
Timing
WHO experts strongly recommend introducing complementary foods to babies at 6 months. This applies only to he althy children,with a body weight corresponding to normal indicators, without pathologies of intrauterine development and malnutrition. Having begun to give the first complementary foods while breastfeeding, the mother of the crumbs should continue to eat fully, include in the diet components enriched with vitamins, minerals and nutrients. After all, the baby still needs milk.
Some experts, relying on the "Methodological guidelines for modern methods of feeding", for babies who are bottle-fed, recommend introducing complementary foods from the age of three months. However, scientific research and experience of pediatricians still make it possible not to fully agree with these recommendations and make some adjustments to them.
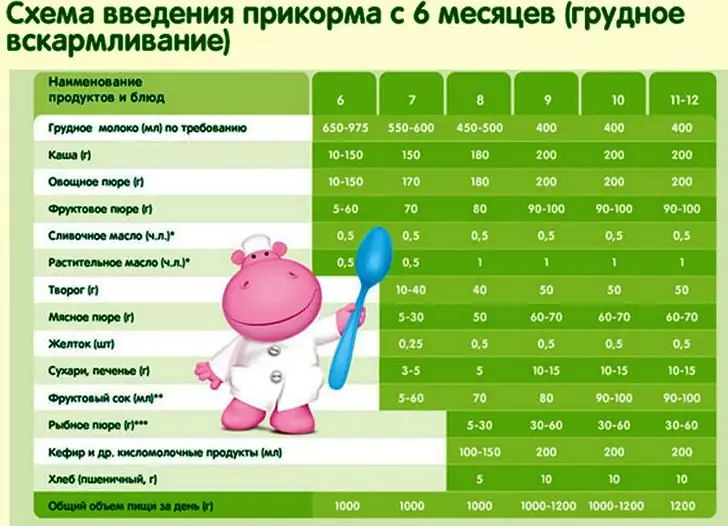
Complementary foods for months while breastfeeding can be represented as follows:

So, the minimum age for a baby to be introduced to complementary foods should be at least four months old. Before the specified period, a baby who is breastfed or fed with an adapted milk mixture is not able to absorb other foods. Conversely, a baby who is introduced to complementary foods too late (after 6 months) will experience a lack of vitamins, trace elements and other nutrients necessary for normal development. These children have a delay in growth, weight gain, the formation of chewing and swallowing skills for eating roughage. Based on the above, we can conclude that the optimal time for the introduction of complementary foods is four and six months of age.
What threatens earlycomplementary foods?
Many parents can't wait to feed their baby delicious. However, it should be understood here that it is better to be a little late with the introduction of new food than to start this process prematurely. So, feeding before the age of four months is not the best way to manifest itself from the digestive tract, which is not sufficiently prepared for the adoption of a new product. Introducing complementary foods too early can lead to the following problems:
- Lack of essential digestive enzymes in the body can cause tummy pain, regurgitation, intestinal colic, problems with stool. In other words, earlier feeding will be at least useless, since the food consumed will not be digested and may cause discomfort to the child.
- Allergic manifestations. Another negative consequence, which is caused by increased permeability of the intestinal walls for allergens and a poorly formed protective system of the baby. This inevitably affects the child's immunity, as a result, he is more susceptible to viral and infectious diseases, more often and longer sick.
- Feeding up to four months of age is somewhat dangerous for the baby if he does not have the swallowing skills to eat thicker foods. Poor or completely undeveloped swallowing reflex in some cases leads to the rejection of such food or causes vomiting.
- Excessive load on the internal organs. Since the liver, kidneys, organs of the gastrointestinal tract have not formed sufficiently, early complementary foodscan lead to the development of chronic diseases.
- Another possible consequence of the introduction of early complementary foods is the reduction of breastfeeding, as a result of which lactation may stop altogether. If the child is artificial, this problem is excluded.
Thus, in order to avoid adverse consequences, what will be the first month of complementary foods should be agreed with the supervising physician.
How do you know your baby is ready?
Many mothers are faced with the question of how to know that the baby can already absorb new food for him?

Here you can focus on the following signs:
- Baby is over four months old and under six.
- There is a decrease in the reflex of pushing food out with the tongue and, conversely, a well-developed reflex of moving food into the mouth and swallowing it.
- Expressed readiness of the baby for chewing function - when a nipple, teether, spoon and other objects get into the mouth, he starts to chew them actively.
- The process of teething has begun or their presence has been ascertained.
- Child can sit alone or with support, has neuromuscular coordination, holds head and neck confidently.
- Baby's ability to express his attitude to the food that is offered to him: leans to the spoon, opens his mouth, purses his lips, throws his head back or turns away if he is full.
- The normal functioning of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract in order to gradually absorb the proposed product - morethick relative to breast milk consistency - no bowel disorder or allergic manifestations to a specific product.
Can semolina
Moms and grandmothers claim that semolina porridge has long been considered a good complementary food. It began to be introduced boiled in milk or water, a liquid consistency. Soviet pediatricians agreed and especially recommended semolina for children with low weight gain. Strictly disciplined parents obeyed the doctors in everything and fed their children with such porridge almost from the age of two months.

In turn, modern experts have a different opinion. For example, gastroenterologists believe that it is contraindicated to give children under one year of complementary foods in the form of semolina porridge. They explain this by the fact that the enzyme system and the gastrointestinal tract of the child are not yet able to absorb it. For underweight children, an exception is made and they are allowed to give semolina from 9 months.
It is not harmful to children, but it is worth knowing that porridge prevents the natural absorption of calcium, which is so necessary for a growing body to form dental, bone and muscle tissue. The best option would be to give her child no more than three times a month until he reaches the age of three. Modern doctors do not recommend that children under 2.5 years of age consume cow's and goat's milk, so semolina is prepared with water or with the addition of an adapted infant formula.
Feeding problems
It happens that a child flatly refuses to try new food from a spoon and pushes everything out of his mouthlanguage. In exceptional cases, complementary foods even cause a gag reflex in the baby, which especially worries young parents. Pediatricians advise not to panic about this, talking about the completely functional origin of such a reaction. As a rule, it is caused by a prolonged period of breastfeeding.

Naturally, it is not worth forcibly stuffing a child, the baby has his own desires and taste preferences. But you can resort to small pedagogical tricks:
- Feed the baby after a long walk when he is hungry enough.
- Take into account his taste preferences, some children are happy to eat porridge, others - fruit or vegetable puree.
- If the new product is not perceived by the child, you should return to your favorite dish, and the one that he refused to introduce again in one to three weeks.
- Feed the child at the common table so that he can see with what pleasure the whole family eats and join the process.
Sometimes the reason for refusal to eat lies in the poor he alth of the child, he may cut his teeth or tummy ache. Very often, with viral infectious diseases in children, poor appetite is observed. Symptoms include: cough, fever, runny nose. They, as a rule, develop later, and the pathology begins to manifest itself as a baby's weakness and lack of appetite. In such cases, the start of complementary foods should be postponed until the child has fully recovered. An unobtrusive approach and patience on the part of parents will gradually allowbaby's diet all the products he needs.
Recommended:
Baby refuses complementary foods: basic rules for the introduction of complementary foods, first products, tips and tricks

Until one year of age, breast milk is the main source of nutrition. It is quite possible that at first the child will not perceive ordinary food and will refuse it in every possible way. Mom should learn about the basic rules for the introduction of complementary foods. And most importantly - to study the psychological aspects of the first complementary foods
Constipation in the baby. Komarovsky E.O. about constipation in infants during breastfeeding, artificial feeding and with the introduction of complementary foods

Such a problem as constipation occurs frequently in infants. Not all parents know how to behave in this case. The famous children's doctor E. O Komarovsky recommends young mothers not to worry, but to carefully monitor the condition of the child
Complementary foods for babies: timing, types of complementary foods, necessary products

Baby's body is developing. He actively moves, sits down, tries to stand up. Weight gain starts to drop. This is one of the signals that it is time to introduce complementary foods. When and how best to do it?
Which porridge to start complementary foods and at what age?

When a new person appears in the family, new parents have many questions. They care about everything related to the baby. Not the last place is occupied by the diet of the baby. In this article, we will consider at what age it is best to start introducing new foods into a child’s diet, and we will also find out what are the best cereals for complementary foods
Complementary foods while breastfeeding. Complementary foods by months - table

With all the advantages of breast milk and its benefits for a growing body, there is still a drawback - the lack of vegetable protein and fiber in its composition, necessary for the full growth and physical development of the child. In this regard, it becomes necessary to introduce complementary foods during breastfeeding when the baby reaches a certain age