2026 Author: Priscilla Miln | miln@babymagazinclub.com. Last modified: 2025-01-22 17:55:22
ICP (infantile cerebral palsy) is a group of diseases characterized by damage to the central nervous system. The main cause of the disease is damage to brain cells, which was caused by oxygen starvation or trauma in the prenatal or postnatal period. At the same time, dysfunction of the muscular and motor systems and impaired coordination of movement and speech are observed.
We will talk about how to determine cerebral palsy in newborns in this article.
Factors that have a destructive effect on the brain

As a rule, the cause of this disease is the pathological processes that occur in the mother's body during pregnancy, and it is worth talking about several problems that have arisen at the same time. The most significant causes for the appearance of cerebral palsy in newborns:
- forced oxygen starvation of the fetus in the womb, caused by a violation of the blood circulation of the brain;
- an acute lack of oxygen during childbirth or immediately after birth (by the way, a special place here is occupied by premature birth duringassisted caesarean section);
- maternal infectious diseases;
- birth trauma.
Cerebral palsy in newborns: symptoms leading to a diagnosis

To cope with this serious problem, it is necessary to start treatment as early as possible (75% of cases of cerebral palsy are reversible when treated before 3 years). That is, attentive parents can notice certain deviations in the child's behavior in time and draw the attention of the local pediatrician to them. And for this they need to remember the symptoms characteristic of the diagnosis of cerebral palsy:
- child by one and a half months, lying on his tummy, does not keep his head up;
- he retains absolute reflexes longer than usual: palmo-oral (if you press the baby on the palms, he will definitely open his mouth) and automatic walking (if the baby is leaned on his legs and tilted forward a little, he starts to sort them out, as if he is walking); these reflexes should be gone by 2 months;
- baby after 4 months no interest in toys;
- baby makes involuntary movements, shudders or freezes in any position;
- often gagging and bad sucking.
CP in newborns: symptoms confirming the diagnosis

A particularly clear example for the detection of cerebral palsy is the constant manipulation of only one handle, while the other is pressed against the body and strongly compressed. It is often difficult for a mother to spread the baby's legs or turn himhead.
Another feature is no less characteristic: the baby, in order to get into the mouth with a pen, turns away from it. Also evident is the inability to sit independently by the age of six months (as a rule, with cerebral palsy this happens only by the age of 3), and such a child begins to walk only at 4 years old.
CP in newborns: symptoms as a prognostic criterion
Parents need to remember that cerebral palsy is a disease that is not prone to progression. In addition, despite the strong lag in the development of motor functions, the psyche of such children does not always suffer. Therefore, the prognosis and effectiveness of treatment entirely depend on the severity of the disease.
Due to the high compensatory capabilities of the child's brain, many consequences of damage can be canceled and, accordingly, the prognosis for the treatment of cerebral palsy in newborns, the symptoms of which are confirmed, can be favorable. The main thing in this case is not to get lost, start treatment on time and be persistent in your desire to see the child he althy. Good luck!
Recommended:
Chickenpox in newborns and infants: causes, symptoms, features of the course, treatment

Chickenpox is believed to be a childhood disease. Indeed, preschool children aged two to six years are mostly affected by it. Most of them suffer from chickenpox in a mild form and receive strong immunity to the virus for life. But what if, in addition to a preschooler, a baby also lives in the house, how to protect him from the disease? We will talk about this and what to do with chickenpox in newborns and infants in our article
Pimples in newborns on the body: causes, diagnosis and treatment methods. Diaper dermatitis in newborns
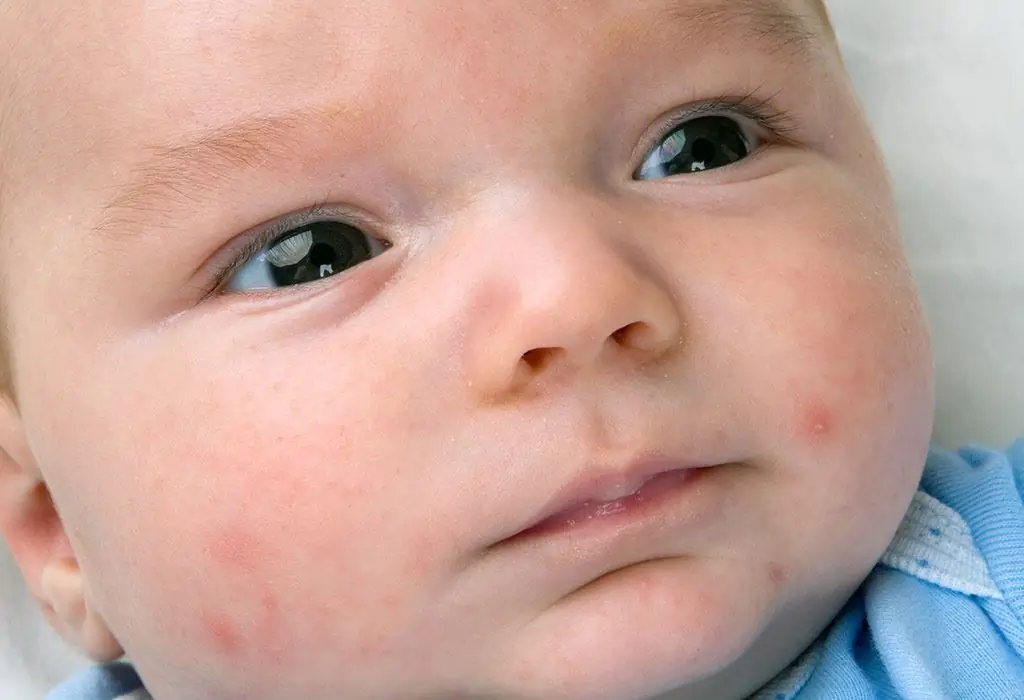
Pimples in newborns on the body are of particular concern to parents. They are red, white, single, large, small, etc. Moms are interested in the causes of pimples, as well as what to do in this situation. There are many known factors that cause acne. Some of them do not require any treatment, while others are an urgent signal to see a doctor
Neonatal jaundice in newborns: causes, symptoms and treatment

The birth of a baby is a great joy for parents. However, sometimes, especially when it comes to the firstborn, it can be overshadowed by a change in the color of the skin and mucous membranes of the child. The phenomenon, known as neonatal jaundice, is common enough that those who are soon to have a baby should learn more about it
Neurology in newborns: causes, signs and symptoms, treatment methods

Neurological problems in newborns are observed in almost 80% of cases. This is a very high figure. Poor ecology, malnutrition, constant worries and psycho-emotional stress during pregnancy often negatively affect the he alth of the unborn child
Intestinal obstruction in newborns: causes, symptoms, treatment methods

Intestinal obstruction in newborns is an unpleasant pathology in which there is a complete or partial blockage of the large or small intestine. It makes it difficult for liquids, food and gas to pass through the standard path, bypassing the intestines. Often the blockage provokes severe pain that comes and goes. Obstruction occurs in one child out of one and a half thousand

