2026 Author: Priscilla Miln | miln@babymagazinclub.com. Last modified: 2025-01-22 17:55:21
The birth of a baby is a great joy for parents. However, sometimes, especially when it comes to the firstborn, it can be overshadowed by a change in the color of the skin and mucous membranes of the child. The phenomenon, known as neonatal jaundice, is common enough that expectant mothers should learn more about it.

Reasons
The appearance of jaundice in newborns is absolutely normal. This phenomenon is observed if the content of bilirubin in the blood of the crumbs due to the breakdown of red blood cells exceeds the norm. It should be understood that, in addition to their own blood cells, the body of the newborn also has to process the residual red blood cells of the mother. Thus, the load becomes significant, and as a result, an excess of bilirubin accumulates, which leads to yellowing of the eye sclera and skin of the baby. At the same time, the child has no other pathologies, he is considered he althy, and he does not need treatment.
Physiological form
Usually, changes in the appearance of the child are observed on the 2-5th day after birth and disappear at 2 weeks of life. At the same time, it is possible to contribute to the speedy disappearance of the symptoms of physiological jaundice, if more often apply the baby to the chest. This will speed up the excretion of the original feces - meconium, with which excess bilirubin is removed from the body. In addition, it is recommended to walk more often with the baby in the fresh air.

Physiological neonatal jaundice of the newborn: causes
As already mentioned, the natural color of the skin and mucous membranes is usually restored by 10-14 days of life. Otherwise, neonatal jaundice is diagnosed. It can be caused by:
- premature baby;
- bilirubin hyperproduction;
- enzymatic immaturity of liver cells;
- reduced ability of blood serum to bind bilirubin.
- pathological neonatal jaundice (prolonged).
The disease can be congenital or acquired.
In the first case, neonatal jaundice may be due to:
- Pathology of the erythrocyte membrane. This disease sometimes appears already in the neonatal period. Over time, the spleen and liver enlarge, and later anemia develops.
- Erythrocyte enzyme deficiency. In this case, jaundice occurs on the second day of life. One of the signs is dark urine.
- Defect in the synthesis and structure of hemoglobin and heme. Appears at 4-6 months of baby's life.

Acquired abnormal neonatal jaundice is of three types:
- hemolytic disease of the newborn, which is the result of an immunological conflict between the blood of the fetus and the mother's blood;
- hemorrhage into the internal organs, or cephalohematoma, during the resorption of which the breakdown products of hemoglobin enter the bloodstream;
- a number of other reasons, such as an increase in the content of erythrocytes in the blood of a child, a syndrome that develops when blood enters the gastrointestinal tract of an infant during childbirth, the presence of an immunopathological disease in the mother, drug hemolysis, etc.
Treatment
As with physiological jaundice, babies are advised to breastfeed more often and take them out into the fresh air. In addition, if the child has neonatal jaundice, then phototherapy is used. It consists in irradiating the crumbs with a photo lamp. Under its rays, bilirubin accelerates in his body, and then it is excreted from the body with urine and feces.
The procedure is as follows:
- the child is completely undressed (if it is a boy, a bandage is applied to the genitals) and placed in a special box for newborns;
- eyes are closed with an opaque mask with an elastic band;
- irradiation is carried out for at least 2-3 hours, interrupted for feeding;
- from time to time the child is turned over so that the photobeams have access to all areas of the skin.
In especially serious cases, when the levelbilirubin is critically high, the session is carried out continuously. At the same time, blood is taken for analysis every hour. The procedure is stopped only when the studies show a satisfactory result for bilirubin.
Contraindication to continue phototherapy is skin redness. However, such phenomena are extremely rare.

OZPK
Treatment of neonatal jaundice in severe cases can be done by exchange transfusion surgery. The indications for this method are:
- unsatisfactory results of laboratory tests of the level of bilirubin in the umbilical cord blood at the time of birth and its constant increase even against the background of phototherapy, etc;
- proven sensitization in the mother and signs of severe hemolytic disease of the newborn in her baby;
- appearance of symptoms of bilirubin intoxication in crumbs.
Medicines select blood components for transfusion strictly individually for a particular baby and taking into account the type of blood incompatibility between mother and child. In addition, FRP is performed only after a successful compatibility test via an umbilical vein catheter. At the same time, you should be aware that even with the right material for the operation and strict observance of sterility, various complications are not excluded. For example, air embolism, cardiac dysfunction, infection, thrombosis, anaphylactic shock, etc.the medical staff must strictly monitor the condition of the baby.

Other methods
Treatment can also be done with medications and infusion therapy. In the first case, "Zixorin", agar-agar, "Carbolen" and "Cholestyramine" are prescribed, which help to free the intestines from bilirubin. Choleretic drugs are also prescribed. As for infusion therapy, it is carried out with sodium chloride and glucose solutions, and with a reduced protein level, an albumin solution is used.
Prevention
Neonatal jaundice, the causes of which are described above, will most likely not occur or its symptoms will disappear faster if the following measures are taken.
- immediately after birth, attach the baby to the mother's breast;
- undress the baby and leave it naked on the diaper for half an hour;
- breastfeed on demand;
- from the first days to walk with the child in the fresh air;
- feed the baby from each breast for at least 7-10 minutes;
- if the baby refuses to suck, then mother's milk should be expressed and given to him from a spoon.

Now you know what neonatal jaundice is. Symptoms of various forms of this disease are described above, therefore, noticing their signs, you can immediately take the baby to the doctor and not lose precious time.
Recommended:
Chickenpox in newborns and infants: causes, symptoms, features of the course, treatment

Chickenpox is believed to be a childhood disease. Indeed, preschool children aged two to six years are mostly affected by it. Most of them suffer from chickenpox in a mild form and receive strong immunity to the virus for life. But what if, in addition to a preschooler, a baby also lives in the house, how to protect him from the disease? We will talk about this and what to do with chickenpox in newborns and infants in our article
Nuclear jaundice in newborns: symptoms, consequences and treatment

Brain damage is a terrible consequence of diseases such as kernicterus
Pimples in newborns on the body: causes, diagnosis and treatment methods. Diaper dermatitis in newborns
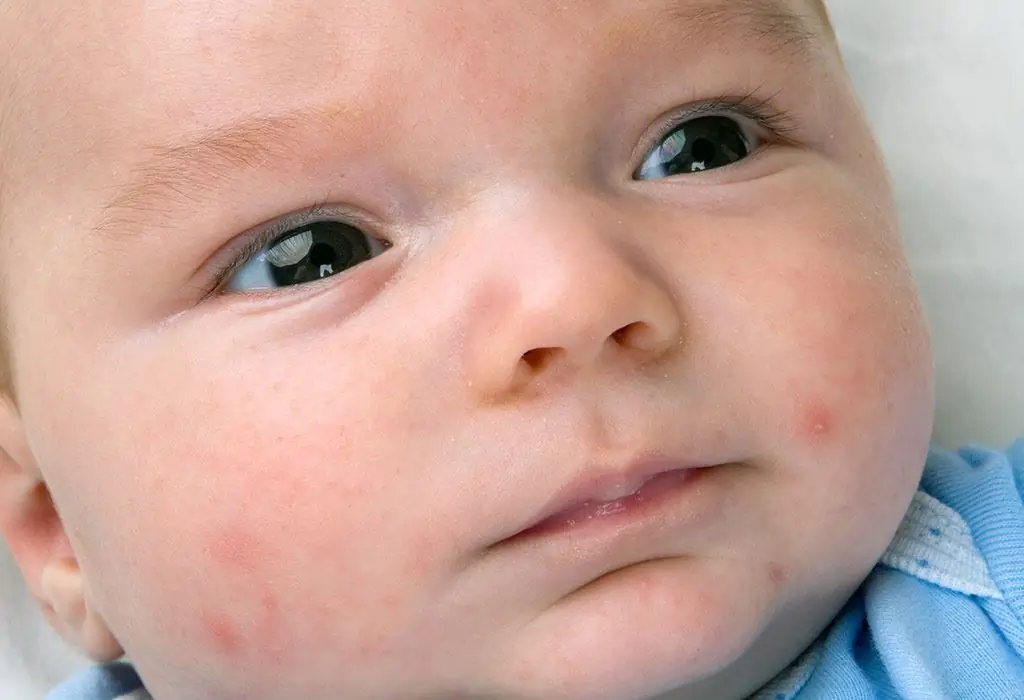
Pimples in newborns on the body are of particular concern to parents. They are red, white, single, large, small, etc. Moms are interested in the causes of pimples, as well as what to do in this situation. There are many known factors that cause acne. Some of them do not require any treatment, while others are an urgent signal to see a doctor
Jaundice in newborns: causes, treatment, consequences, reviews

Jaundice in a newborn is not a separate disease, but only signals a malfunction in the body. The skin becomes yellowish due to the accumulation of bilirubin in them - a bile pigment
Neurology in newborns: causes, signs and symptoms, treatment methods

Neurological problems in newborns are observed in almost 80% of cases. This is a very high figure. Poor ecology, malnutrition, constant worries and psycho-emotional stress during pregnancy often negatively affect the he alth of the unborn child

