2026 Author: Priscilla Miln | miln@babymagazinclub.com. Last modified: 2025-01-22 17:55:24
Not everyone is familiar with the term prenatal screening. However, people who work in the field of he althcare know almost everything about it. Moreover, the term "screening" itself comes from the English word screening, which means selection or sorting. In other words, this refers to the process of choosing or rejecting something.

Remarkably, the term screening is used in many areas of human activity. In economics, this word means identifying reliable partners. As for he alth care, this means examining people in order to detect symptoms of a disease in the early stages.
In particular, prenatal examination is a whole range of studies that every pregnant woman undergoes. They allow you to detect all sorts of defects in the development of the child. Based on all the information received, both the expectant mother and the doctor are aware of the progresscourse of pregnancy. And if there are risks, take the necessary measures in a timely manner.
General information
Let's take a closer look at exactly what prenatal screening is. After all, such a survey is carried out not only among expectant mothers, but also among all the rest, depending on age. And the very word "prenatal", in turn, means prenatal. Such a complex of medical research includes not only the delivery and processing of laboratory tests, but also hardware examinations (ultrasound).
The importance of prenatal research is difficult to overestimate or underestimate, because it allows you to control the development of a child who is still in the womb. Moreover, it is possible not only to detect the deviations themselves, but also to identify all possible risks of pathologies. Only on the basis of the data obtained from screening, the doctor makes responsible decisions in the future. That is, whether additional examination is needed.
Most expectant mothers fear that waiting for test results can unwittingly trigger stress. It is worth noting that a woman has the right to refuse this kind of screening if there is no desire or confidence in such procedures.

But if you look at everything from the other side… If any anomaly in the development of the fetus is detected in the expectant mother during the calculation of risks during pregnancy at 1 screening, she faces a difficult choice: continue to bear a child with a pathology and raise him or terminate the pregnancy.
The essence of screening
Screening aims to inform the woman about the nature of the pregnancy. And if the expectant mother receives unwanted information, she will have time to mentally prepare for the birth of a special child. If there are no deviations, then there is no cause for concern either.
However, there are specific indications for prenatal screening:
- Women over 35.
- If close relatives have a genetic predisposition to any disease.
- Families where children with genetic and chromosomal abnormalities or congenital malformations have already been born.
- If the woman has previously had an abortion.
- Mother had two or more miscarriages in a row.
- Conceived from a close relative of the same blood.
- Medications for the period of the first trimester (up to 13-14 weeks), which are prohibited for pregnant women.
- One of the partners was exposed to radiation shortly before conception.
This is a kind of prenatal examination risk group. Only here it should be clearly understood that this does not include those women who are threatened by something during the necessary examinations, as it might seem at first glance. Everything is different here, because these procedures, which are included in the comprehensive prenatal screening, are completely safe.

The risk group includes those women who, for whatever reason,there is a high risk of developing anomalies in a child. In this regard, the course of pregnancy deserves increased attention.
What else needs screening
It is unlikely that anyone wants to argue with the importance of screening, although there may be those who wish. That's just for this it is worth giving a strong argument in favor of the need to undergo scheduled examinations. In particular, we are talking about the identification of many serious pathologies, which may include:
1. Down syndrome - a similar chromosomal disorder can be detected in the first or second trimester.
2. Edwards syndrome - can be detected at the same gestational age as the disease mentioned above. This chromosomal change is considered a severe pathology, which is often incompatible with life or ends in mental retardation.
3. Anencephaly - prenatal pregnancy screening will detect this pathology, but only for the period of the second trimester. In this case, the development of the brain and spinal cord is disrupted.
4. Cornelia de Lange syndrome - belongs to the category of hereditary diseases. His symptoms are mental retardation and multiple developmental anomalies.
5. Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder. The result can be mild - minor defects on the physical level and violations in the intellectual plane. At the same time, there may be a severe form, which is expressed in a deep degree of mental retardation and severe physical defects.
6. non-molar triploidyis a rare chromosomal anomaly that does not end well and often leads to fetal death in early pregnancy or it all ends in stillbirth. But even if the child survives, there will be many violations in his body, as a result of which he will not be able to live for a long time - just a few weeks.

7. Patau syndrome is another chromosomal pathology that cannot be hidden from prenatal screening. Otherwise, it is called as trisomy 13 or trisomy D. The frequency of the appearance of children with a similar anomaly is 1: 7000-10000. Often, with such a deviation, miscarriages or stillbirths also occur. However, if a child is lucky to be born, then he lives no more than a week, since the work of the brain, the heart is disturbed, there are pronounced defects in the spine and other equally serious pathologies.
It is the prenatal examination that can detect the listed pathologies in the fetus. For the most part, when there is a dangerous risk, the decision is made to terminate the pregnancy for medical reasons.
Indications for screening
Probably, many women, having heard about screening, begin to think about whether there are indications and contraindications here. Most likely, the foreign origin of the word affects. But an important point should be clarified - screening is understood as a whole range of studies, and the most elementary ones (blood test, ultrasound). As for the timing of prenatal screening, it is usually carried out as soon as the pregnant woman gets upaccount.
In other words, the very fact of a successful conception and bearing of a child is already becoming an indication for screening. And since all manipulations are completely safe, there are simply no contraindications here. There is only one important point - a woman must undergo any kind of examination while being he althy.
If there is a disease, screening results can be distorted. This applies not only to acute respiratory illness (colds), but also to viral infections, including tonsillitis.
Therefore, before undergoing screening, a woman should visit her attending gynecologist, ENT doctor, therapist. Sometimes it is worth visiting other narrow specialists. This will allow women to make sure that they are completely he althy and nothing can distort the results of screening studies.
Types of prenatal screening
There are three main types of screening we are considering, as well as three main periods of pregnancy (trimesters). For clarity, the table below is shown in the photo.

There are different tests:
- Molecular - is indicated in cases where there are people in the family of mom or dad who have been diagnosed with one of the following diseases: cystic fibrosis, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, hemophilia A and B, including other similar pathologies. If the patient wishes, then the test for the presence of these diseases can be done before the onset of pregnancy or during childbearing. The research material isblood from a vein.
- Immunological (prenatal genetic screening) - this test also requires venous blood. Its purpose is to determine the blood group, Rh factor, as well as TORCH infections: rubella, cytomegalovirus, chicken pox, toxoplasmosis, herpes. Experts recommend conducting this study twice during the entire period of pregnancy - I and III trimester.
- Cytogenetic - a geneticist does this research, which does not require any equipment. The examination is conducted in the manner of communication between a doctor and a patient, during which a specialist can find out if a woman or her husband has hereditary diseases. If there are any, this is already an occasion for a more detailed study. This test should be carried out when planning a child or during the first trimester.
As you can see, these tests are rather an addition to the main screening, which includes two more studies: ultrasound and blood biochemistry. But, in addition, invasive procedures are carried out: chorion biopsy and amniocentesis. Only they are appointed in extreme cases.
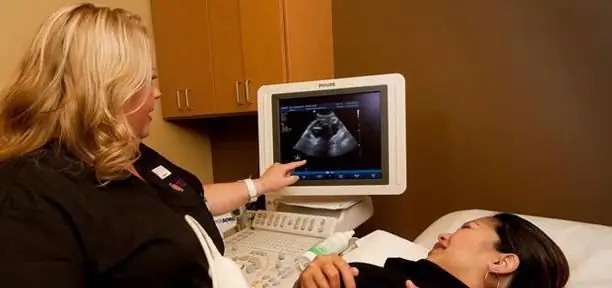
Ultrasound screening
During the entire pregnancy, ultrasound should be performed at least three times:
- from 10 to 14 weeks;
- 20 to 24 weeks;
- from 32 to 34 weeks.
This applies to the most basic dates, but if necessary, the doctor can prescribe any other time for this study. This is often done to clarify an earlier diagnosis.

The advantage of thisnon-invasive prenatal screening in that it allows you to visually identify any abnormalities in the development of the child, including growth retardation, which is especially important. Every year, up to 3 children out of every thousand newborns are found to have a gross form of developmental pathology that cannot be surgically corrected.
Biochemical research
Biochemical screening analyzes hormones, which makes it possible to identify possible genetic abnormalities at an early stage. The most dangerous pathologies of all others are Down syndrome, Patau and Edwards. During the first examination, you can easily detect the characteristic signs of Down syndrome deviation. This is only achieved only in conjunction with the first screening with ultrasound.
And they are:
- Significant excess of hCG levels.
- Thickened collar space.
- No new bone at 11 weeks.
During the second trimester, this syndrome is detected by other signs: a more reduced level of AFP against the background of a high concentration of hCG. Therefore, blood biochemistry is done at least twice: from 10 to 14 weeks and from 16 to 20 weeks.
I screening
How and when is such an important examination carried out? According to the table above, the first prenatal screening is carried out - in the 1st trimester. That is, starting from the 11th week of pregnancy to the 13th. During the visit to the gynecologist, who will conduct further monitoring, the woman will undergo a mandatory examination:
- growth measurement;
- determination of weight (which will allow us to judge the nature of weight gain);
- blood pressure measurement;
- complete full medical history including any chronic and past illness.
- If necessary, advice from a highly specialized specialist will be required.
Ultrasound is mandatory, during which the state of the chorion, ovaries and uterine tone are assessed. Subsequently, it is from the chorion that the placenta will form. In addition, ultrasound at this time may show a singleton or multiple pregnancy, including the development of the spinal cord, brain and limbs of the fetus (or both children).
Besides this, at the prenatal screening of the 1st trimester, you also need to pass two tests: urine and blood. The latest study will allow not only to determine the group and the Rh factor, but also other risks like HIV, hepatitis and syphilis.
Second screening
The second screening takes place at the end of the first half of the entire pregnancy - from 15 to 20 weeks. With this examination, those risks that were only suspected during the first examination are now either confirmed or refuted.
And if chromosomal abnormalities are found in the fetus during prenatal biochemical screening, the woman will be asked to terminate the pregnancy for medical reasons, since the chromosomal pathology is not yet curable. In this case, the future mother faces a very crucial moment. Preservation of pregnancyend in the birth of a child who will later be disabled or completely unviable.
However, if neural tube defects are found during the second screening, they can still be eliminated completely or minimized. As for the procedures, an abdominal ultrasound is performed and blood is taken for biochemical analysis.
Ultrasound will show what position the child has taken, his anatomical development. In addition, the necessary measurements will be taken:
- limb length;
- head volume;
- chest volume;
- abdominal volume.
As with the first screening, this information will make it clear whether the fetus develops skeletal dysplasia or not. Other important parameters are also being studied: the development of the brain, the formation of the bones of the skull. The state of the organs of the cardiovascular system (CVS) and the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) is assessed. All this makes it possible to judge the presence of any pathology or its absence.
Biochemical blood test is also referred to as a "triple test". During it, the amount of the main hormones produced in the female body only during pregnancy is estimated - these are hCG, AFP. Comparison of the data obtained with the standards makes it possible to judge the development of the process of bearing a child. And if there are any anomalies, then it will be immediately visible to a specialist.
Features of III screening
The third screening is done between 30 and 34 weeks of pregnancy. Its main task is to identify some risks:
- preterm birth;
- probability of complications during childbirth;
- identifying indications for caesarean section;
- detection of intrauterine defects;
- detection of pathologies in the development of the fetus.
According to the decoding of prenatal screening, the last two deviations appear only in the later stages of pregnancy. As for the necessary procedures, there are three of them:
- Ultrasound.
- Doppler study.
- Cardiotocography (CTG).
During a routine ultrasound examination, the condition of the fetal organs is assessed, amniotic fluid is examined, including the condition of the placenta, umbilical cord, cervix and its appendages. All this makes it possible to determine the presence of obstetric complications during childbirth and to identify malformations in the development of the fetus.
Doppler is a type of ultrasound and its main task is to determine the he alth of the child's circulatory system, including the uterus and placenta. With the help of this examination, it is possible to detect malformations in the development of the heart, the maturity of the placenta, its performance, the likelihood of entanglement of the fetus with the umbilical cord. You can also determine whether there is enough oxygen supplied to the fetus, or you can judge its deficiency.

Cardiotocography records the heart rate (HR) of the fetus, its mobility. In addition, you can find out what tone the uterus is in. With the help of this study, it is possible to detect deviations of the cardiovascular system, and to reveal the fact of oxygenfasting.
Prenatal screening results
Deciphering the results of all conducted and necessary studies should be done only by a doctor and no one else. And in order for them to be reliable, some factors should be taken into account:
- gestation period;
- how old is the expectant mother;
- presence of obstetric and gynecological pathologies;
- does a pregnant woman have a bad habit, and any;
- what kind of lifestyle does the expectant mother lead.

At the same time, even when all these and other factors are taken into account, the results may still turn out to be false (positive or negative). And there are other reasons for this. First of all, this applies to overweight women, IVF, multiple pregnancy, acute chronic stress, diabetes mellitus, untimely amniocentesis immediately before blood sampling (a week should pass, not earlier).
Recommended:
When is the second screening done? Terms, norms, decoding

Examination of a woman's body during pregnancy is mandatory. The performed medical research procedures allow you to monitor the development of the fetus in the womb and, if necessary, correct possible deviations from the norm. This makes it possible to carry a fully developed baby and prevent miscarriage
How is the gestational age calculated by week, from what day?

Pregnancy and planning is not easy. And if a girl managed to conceive a baby, you need to know how to calculate the gestational age. Some people have problems with this task. This article will talk about calculating the gestational age and determining the date of conception of a child
Artificial childbirth: how are they done and what are the consequences?

Pregnancy is the happiest period in every woman's life. How nice it is to realize that a new life is growing inside you, which will soon delight you with its successes. The natural end of pregnancy is the independent discharge of water and the birth of a baby. Unfortunately, under unfavorable circumstances, gynecologists decide to induce artificial labor. In what cases does this happen? What could be the consequences? More about everything in this article
Norm for screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester. Screening of the 1st trimester: terms, norms for ultrasound, ultrasound interpretation
Why is 1st trimester perinatal screening done? What indicators can be checked by ultrasound in the period of 10-14 weeks?
Prenatal bandage for pregnant women: types, recommendations, reviews

Within the framework of this material, we will consider a prenatal bandage, as well as the need for its use. Feedback from women will help to conduct the most objective review

