2026 Author: Priscilla Miln | miln@babymagazinclub.com. Last modified: 2025-01-22 17:55:26
The preliminary period is contractions in the lower abdomen during pregnancy, which are accompanied by minor pain and muscle tension. They are irregular. Such contractions are the precursors to childbirth. Under normal conditions, the preliminary period of labor should take approximately 6-8 hours. However, in some cases this period may be extended. This can happen for various reasons. In this case, there is a pathology of labor, requiring the immediate intervention of doctors. Since the consequences of a protracted preliminary period can be very serious for both the mother and the child: from severe ruptures in a woman in labor and ending with the death of the fetus.
The concept of a pathological preliminary period

The physiology of each woman is individual. In some cases, this period can be delayed for several hours, and sometimes for several days. This leads to exhaustion of the woman, loss of sleep, accumulation of severe fatigue by the time of childbirth. In this case, there is a pathological preliminary period of childbirth, that is, the prenatal period,which dragged on. It is characterized by irregular painful contractions that do not lead to changes in the cervix, but only deplete the woman's body.
The essence of the anomalous preliminary period
The main essence of the pathology can be expressed as follows:
- Physiological preliminary period is dragging on.
- Myometrium tone increases.
- Internal os is shrinking.
- There are contractions of the lower uterine segment.
- Muscle fibers are arranged in a circle, transversely and in a spiral;
Reasons
As a rule, the pathological preliminary period causes the presence of disorders in the body of the woman in labor. The main reasons can be divided into three groups:
OB:
- Presence of polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios.
- Multiple pregnancy.
- The fetus is in the wrong position in the womb (breech presentation).
- The placenta is low.
Psychoemotional:
- Woman is afraid of childbirth.
- Negative attitude.
- Neurosis and strong emotional stress.
- Physical fatigue of the patient.
- Age of the nulliparous woman (fear of the outcome of childbirth if the pregnancy is too early or late).
Physiological:
- A woman in labor has a narrow pelvis.
- Previously, surgical interventions were performed in the uterus (presence of scars after caesarean, etc.).
- Disturbances in the endocrine system (obesity, anorexia, etc.).
- Labile nervous system.
- Diseases of the kidneys, heart,liver and other organs.
- Inflammation of the uterus.
- Preeclampsia.
- Multiple abortions.
- Miscarriage.
Symptoms
The following symptoms help to recognize the pathology of the prelimirous period:
- The uterus in the preparatory and preliminary period is painfully reduced, while contractions are not regular. They can occur both during the day and at night. For a long time, labor does not begin.
- Increased uterine tone and excitability.
- The uterus does not open, it continues to be dense and long.
- The presenting part of the fetus is not pressed against the woman's small pelvis.
- Due to uterine hypertonicity, it is difficult to palpate the fetus.
- The uterus has been contracting monotonously for a long time. The strength and frequency of contractions do not change. The harbingers and the preliminary period are long-lasting.
- A woman's mental state worsens, she becomes whiny and irritable, she becomes uncertain about the successful completion of childbirth.
Types of pathology

Pathological preliminary period can be of two types:
- In the first case, the muscles of the uterus are not relaxed, the muscle fibers of the uterus correspond in density to the "mature" cervix, oligohydramnios, flat amniotic sac.
- In the second case, the cervix is "immature", has an oval shape, the presenting part of the fetus is not adjacent to the entrance to the small pelvis. Most often this situationobserved when the fetus is overcarried.
Duration
The duration of the abnormal preliminary period, depending on the individual characteristics of each woman, can vary from 6 hours to 24-48 hours. For some women, it can take several days.
Possible consequences

Pathological preliminary period in most cases leads to complications in the course of childbirth. In many women in labor, labor activity proceeds abnormally. Specifically:
- The generic activity is weak. This condition is characterized by insufficient strength of uterine contraction, large intervals between contractions, the cervix dilates slowly, the progress of the fetus is delayed.
- Patrimonial activity is discoordinated. It is manifested by erratic contractions of the uterus. There is no synchrony in the contraction and relaxation of individual sections. As a result, contractions are accompanied by severe pain, become frequent and uneven, which exhausts the woman in labor and does not allow her to relax.
- Patrimonial activity proceeds rapidly. This anomaly is characterized by very strong and sharp contractions and attempts. As a result, childbirth occurs very quickly (up to 5 hours). This can lead to ruptures of the vagina and perineum in parturient women, severe bleeding. The fetus may develop hypoxia. Rapid labor can result in birth injury to the fetus.
- Uterine tetanus is a rare anomaly. In this case, there is a state when the uterus does not relax at all. Occurs when multiplepacemakers in different parts of the uterus. It leads to a violation of uterine contractions and stop labor. The fetus may develop hypoxia, which can lead to cardiac dysfunction.

The following consequences of an abnormal course of labor may develop:
- Untimely removal of amniotic fluid.
- The appearance of meconium at the very beginning of contractions, which means "distress" of the fetus.
- Surgical delivery.
- Application of obstetrical forceps.
- Severe abnormal bleeding.
- In the postpartum period, purulent-infectious diseases develop.
- Fetal hypoxia and the birth of a child with cardiac disorders or coronary disease.
Diagnosis

If you suspect that the preliminary period is abnormal, you should immediately contact an obstetrician-gynecologist. He must do an external examination. Palpation helps to determine the high or low location of the fetus. If the fetus has not descended, this indicates the presence of a pathology of labor activity. Also, the pathology can be judged by the presence of strong tension in the muscles of the vagina, the immaturity of the uterus for childbirth and spasms.
The diagnosis of the pathology of the preliminary period is based on clinical and laboratory studies, which allow us to conclude that the acetylcholinesterase activity of erythrocytes decreases, the level of adrenaline and noradrenaline hormones increases in the blood.
An instrumental study is possible. To do this, do cardiotocography. With it, you can register the strength and duration of contractions.
Pathological preliminary period: treatment

With an immature cervix and the absence of independent development of labor, there is a picture of post-pregnancy. Therapy in this case will be prescribed taking into account the pathogenesis of the pathology. The goal of treatment will be to accelerate the maturation process of the uterus. The following treatments may be used:
- Electroanalgesia.
- Electrorelaxation of the uterus.
- Treatment with medications: antispasmodics, analgesics, prostaglins E2.
If the patient has severe fatigue and increased nervousness, then she is prescribed drug sleep as a treatment. Sedatives are also prescribed.
The positive result of treatment is reflected in the abrupt onset of regular contractions. Or in the maturation of the body for childbirth. When the uterus becomes "mature", the fetal bladder is opened and regular contractions begin within two hours. If labor does not begin, then prostaglandins are administered intravenously.
In case of ineffective treatment, along with other complications (obstetric history, large fetal size, breech presentation, OPG-preeclampsia, the onset of fetal hypoxia), an emergency caesarean section is performed.
Approaches to the management of pregnant women who have a pathological preliminary period
There are two approaches:
- Fullpeace.
- Induction of labor with oxytocin.
Both methods are aimed at eliminating violations in labor activity. A successful outcome of the case is observed in 85% of cases. When choosing a method, the following features of the pathology are taken into account:
- The degree of anxiety and fatigue of the patient.
- The reason for the complication.
- Choosing a method that is more convenient for the patient and obstetrician.
When choosing the approach, which consists in observing the complete rest of the pregnant woman, she is injected intramuscularly with 0.015 g of morphine. Then secobarbital inside 0.2 g. This option is quite effective. As a rule, after the introduction of morphine, the patient falls asleep within an hour. After 4-5 hours of rest, during which the exhausted body regains strength, the woman wakes up either without any signs of childbirth, or with active labor.
When choosing the second path, i.e. stimulation with oxytocin, it is worth avoiding the opening of the fetal bladder. Caesarean section is justified only in the most severe cases.
Prevention

The main preventive measures to prevent the pathology of the preliminary period are:
- Timely consultation with an obstetrician.
- Passing all necessary tests.
- Following the doctor's prescriptions regarding the regimen and nutrition.
- Psychological and physical preparation of a pregnant woman for childbirth.
A competent obstetrician-gynecologist should keep women under control,who are at risk for this pathology. Namely: primiparas under the age of 17 and after 30 years, as well as women with diseases of certain organs (liver, kidneys, heart).
So, the pathological preliminary period is one of the types of anomalies in labor activity. It occurs quite often. However, thanks to modern medicine, in 85% of the timely intervention of doctors, childbirth ends safely. Therefore, when the first signs of pathology appear, it is necessary to immediately contact a competent obstetrician-gynecologist. The consequences of an abnormal preliminary period can be very serious, up to fetal hypoxia, the appearance of disturbances in the functioning of its internal organs, and death. Properly prescribed treatment will help save the life of both mother and child.
Recommended:
Hernia in a puppy: causes, symptoms, treatment, recovery period and advice from veterinarians
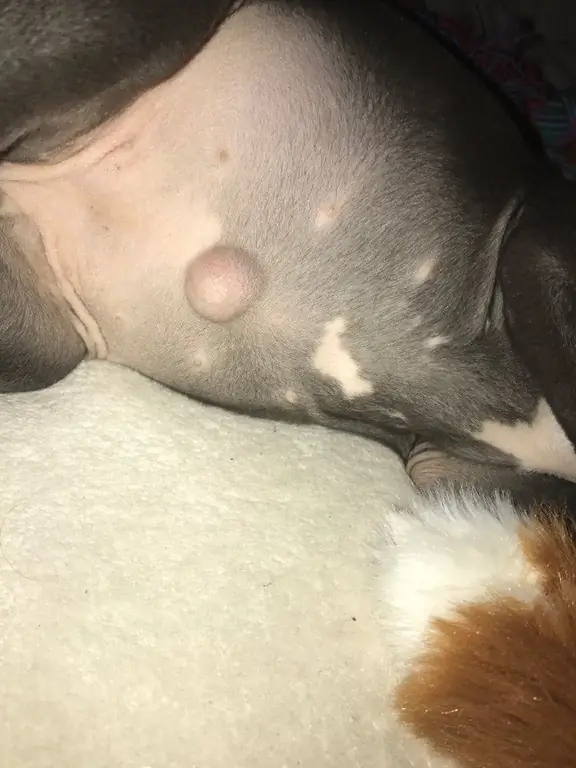
The occurrence of an umbilical hernia in a puppy is a fairly common pathology. With this defect, the internal organs (uterus, intestinal loop, omentum) fall out into the hole that has appeared in the lower abdomen. In most cases, the disease is hereditary
How many days can I get pregnant after my period? How fast can you get pregnant after your period? Chances of getting pregnant after period

Pregnancy is a crucial moment for which every woman wants to be ready. To determine the probable moment of conception, it is necessary to know not only the time of ovulation, but also some features of the human body
Hyperexcitability in infants: causes, symptoms, treatment, recovery period and advice from the best pediatricians

Hyperexcitability in infants is a fairly common problem today. The treatment process includes quite a lot of different elements that give results only when used together. The task of parents is not to miss the moment of healing
Cerebellar ataxia in cats: causes, symptoms, treatment, recovery period and advice from veterinarians

If a little kitten staggers when walking and falls, it always alarms the owner. The situation seems especially strange when there are no other he alth problems in the pet at the same time. The kitten has a good appetite, he is mobile and active, does not make a plaintive meow. But he is not able to walk normally, as a rule, from his very first steps. This may be a manifestation of cerebellar ataxia in cats
Cat sick: causes, symptoms, first aid, treatment, recovery period and veterinarian advice

Probably, every person in whose house a cat lived or lives has at least once encountered her vomiting. This is primarily due to the fact that the part of the cat's brain, which is responsible for the gag reflex, is much better developed than in humans. Therefore, such a nuisance happens to cats quite often. Let's try to find out why the cat is sick, and how the owner can help her in this situation

