2026 Author: Priscilla Miln | miln@babymagazinclub.com. Last modified: 2025-01-22 17:55:27
A pregnant woman faces many dangers. Some of them are preeclampsia and eclampsia - pathological conditions that occur in expectant mothers. In our article, we will not talk about independent diseases, but rather about organ failure syndromes, which is accompanied by a partial lesion of the central nervous system to a greater or lesser extent. You will learn about the causes of eclampsia and preeclampsia, first aid and the likely consequences of this problem right now.
What is this pathology
In a non-pregnant woman or men, such disorders cannot occur. The thing is that the problem originates in the “pregnant - placenta - fetus” system. No doctor is still able to name the exact causes and describe the pathogenesis of the development of this disease, but nevertheless, we will talk about the most likely factors provoking the syndrome in the next section.
According to medical scientists from Western countries, preeclampsia and eclampsia are syndromes that occur as a result of the progression of hypertension. In domestic medical science, not so long ago, there was a slightly different position, according to which both syndromesare considered varieties of preeclampsia.
Eclampsia and preeclampsia develop in pregnant women during the second trimester, usually after the 20th week. Characteristic signs of multiple organ failure, typical of preeclampsia, are persistent arterial hypertension, edema of the body and limbs. The presence of protein in the urine may indicate the development of the syndrome - doctors call this proteinuria.

Unlike pre-eclampsia, eclampsia is accompanied by more serious disorders that lead to damage to the cerebral hemispheres. The patient may experience a coma on the background of a hypertensive crisis. Very characteristic of eclampsia are convulsions, confusion. In the absence of proper medical care, a woman is in danger of death.
Disease classification
Based on the typology established by WHO, multiple organ failure syndrome (preeclampsia) can be mild or severe. The initial stage of the development of this pathology includes gestational hypertension, which is an exacerbation of the chronic form of the disease, provoked by gestation. Diagnosed pre-eclampsia in the majority of cases precedes eclampsia.
Russian obstetrician-gynecologists divide eclampsia into several varieties, depending on the moment it developed:
- during pregnancy - the most common course of the syndrome (occurs in 80% of all cases of eclampsia);
- during childbirth - in the process of childbirth, manifestationsyndrome is diagnosed in every fifth or sixth woman;
- after childbirth - pathology occurs within a day after labor, accounting for about 2% of cases.
Based on the content of medical protocols, eclampsia and preeclampsia are characterized by exactly the same symptom complexes. In addition, the treatment of mild and severe multiple organ failure will be no different. For this reason, the classification and typology of eclampsia is not of fundamental importance to the doctor. The only thing that may depend on the treatment regimen in the event of a syndrome is one of the forms of the disease:
- typical, which is characterized by hypertension (blood pressure exceeds 140/90 mm Hg), body edema, increased cerebrospinal fluid pressure and protein content in the urine (0.6 g / l or more may indicate eclampsia);
- atypical, developing during difficult labor in women with a weakened central nervous system (cerebral edema, non-critical arterial hypertension, increased intracranial pressure);
- uremic - the likelihood of this form of the syndrome is high in expectant mothers with a history of chronic kidney and urinary system diseases before pregnancy.
Provoking factors
As already noted, the causes of eclampsia and preeclampsia are currently practically unknown, which makes it impossible to name them with accuracy. With absolute certainty, doctors can only say one thing - this condition can develop exclusively in pregnant women and not inmore.

There are about three dozen different hypotheses and assumptions about the causes of the syndromes. The most predictive and realistic are several of them:
- genetic disorders;
- thrombophilia, including antiphospholipid syndrome;
- chronic infectious diseases (Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, etc.).
Complicates the situation and the inability to know for sure whether this problem will occur in a woman during the period of gestation in the absence or presence of these factors. Physicians are also aware of the fact that fetoplacental insufficiency serves as a trigger for the development of eclampsia. Doctors consider other risk factors predisposing to the disease:
- presence of references to pre-eclampsia or eclampsia in protocols for the management of childbirth and pregnancy prior to the current one;
- presence of the syndrome in the mother or other blood relatives;
- multiple or first pregnancy;
- age over 40;
- long interval between previous and current ongoing pregnancy (more than 8 years);
- chronic arterial hypertension;
- diabetes mellitus;
- cardiovascular disease.
Features of symptoms
The main signs of eclampsia and preeclampsia in pregnant women are three manifestations:
- swelling of limbs and body;
- significant increase in blood pressure;
- presence of protein inurine.
To diagnose multiple organ failure syndrome in a future mother, any symptom in combination with hypertension is enough.
Edema in this disease can be localized in different places and have different severity. In some women, swelling can occur only on the face, in others - on the legs, and in others - throughout the body. Unlike edema, which occurs in most pregnant women, eclampsia edema does not become less pronounced after a long stay in a horizontal position. With pathological edema due to preeclampsia, the patient is rapidly gaining weight in the second trimester.

In addition to swelling, increased blood pressure and proteinuria, the possibility of additional symptoms of the disease is not excluded. Due to damage to the central nervous system caused by hypertension, manifestations such as:
- severe headache;
- blurred vision, veil, flies before the eyes;
- epigastric pain;
- dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea);
- muscle hypertonicity;
- reduction in urine output (less than 400 ml per day);
- pain on palpation of the liver;
- thrombocytopenia;
- fetal growth retardation.
The first symptoms of severe preeclampsia are an unconditional reason for hospitalization of the patient in an obstetric hospital. A pregnant woman is shown treatment, the purpose of which isnormalization of pressure, removal of swelling of the brain and prevention of the development of eclampsia.
Toxicosis in preeclampsia does not pose a particular threat and does not affect the course of the syndrome. Eclampsia, unlike preeclampsia, is manifested by convulsive seizures caused by brain damage due to swelling of the hemispheres and increased CSF pressure. Thus, convulsions can be considered the main sign of eclampsia, which can be:
- single;
- serial;
- provoke coma after seizure.
Sometimes the loss of consciousness in patients is not preceded by convulsive attacks. A sudden worsening headache, insomnia, a sharp jump in pressure signal an impending deterioration in the condition.
Cramps often begin with visually imperceptible twitches of the facial muscles, which gradually move to the muscles of the whole body. Most often, after the end of a convulsive seizure, consciousness returns, but the patient is not able to talk about her feelings, since she does not remember anything. Convulsions against the background of eclampsia are repeated when exposed to any stimulus, be it a bright light, a loud sound, pain, or internal experiences. The reason in this case is the increased excitability of the brain, provoked by swelling and high intracranial pressure.
How to diagnose the syndrome
Pre-eclampsia and eclampsia of pregnancy are among the most serious problems in obstetrics. To prevent deterioration of well-being, it is important to monitor blood pressure and periodically undergo clinicalresearch:
- general urinalysis (for proteinuria);
- blood test to determine the level of hemoglobin, the number of platelets and red blood cells, the clotting period;
- electrocardiogram;
- biochemical blood test for the concentration of urea, creatinine, bilirubin in it;
- CTG and fetal ultrasound;
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the uterus and placenta.

All of these diagnostic procedures allow early detection of preeclampsia and eclampsia. Emergency care in the clinic will be provided to a woman, regardless of the severity and severity of symptoms. However, people close to the pregnant woman also need to know how to act in the event of an eclamptic attack.
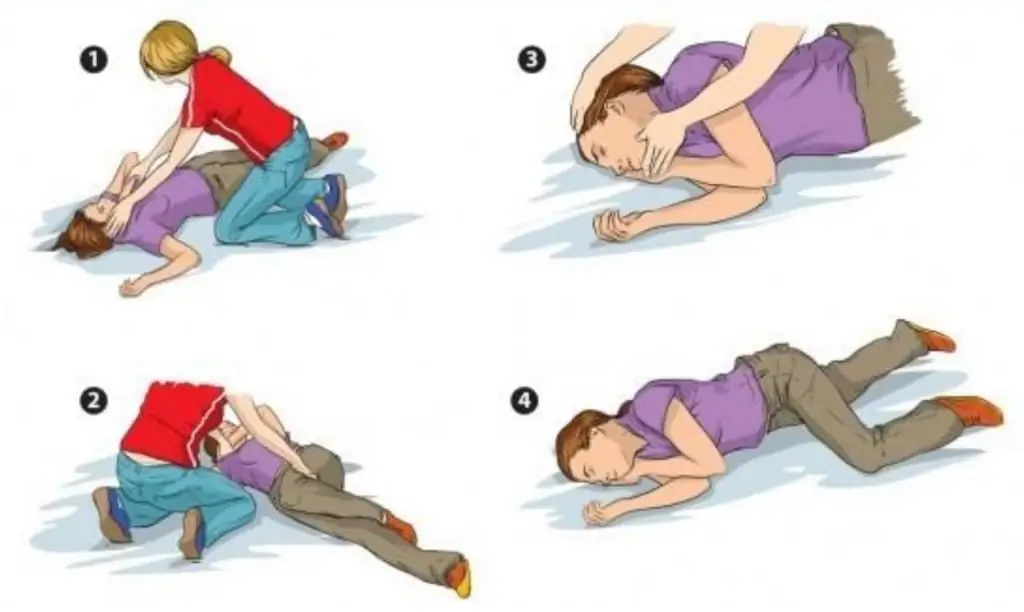
Before the ambulance arrives
The emergency care algorithm for eclampsia and preeclampsia is of particular importance to the patient. First of all, a woman needs to be laid on her left side - this minimizes the risk of choking with vomit, as well as getting blood and stomach contents into the respiratory tract and lungs. The patient must be carefully transferred to a soft surface (bed, mattress or sofa) so that during the next convulsive attack she does not inflict accidental injuries on herself. During a seizure, it is not necessary to hold the patient, to squeeze her arms and legs. Whenever possible, it is important to provide oxygen through a mask during convulsions (optimum rate is 4-6 L/min). As soon as the cramp is over, it is necessary to clean the mouth and nasal passages from mucus, vomit, blood.

Anticonvulsant treatment
First aid for eclampsia and preeclampsia is not enough to alleviate the patient's condition. It is impossible to stop seizures without drugs in this syndrome.
Ambulance specialists administer sick magnesium sulfate immediately upon arrival. Moreover, the manipulation should be carried out in stages, in compliance with the correct sequence. A solution of magnesia of 25% concentration in the amount of 20 ml is injected intravenously. The medicine is given by drip for 10-15 minutes, after which the dosage is reduced. For maintenance therapy, 320 ml of saline is diluted with 80 ml of 25% magnesium sulfate. The optimal rate of drug administration is 11-22 drops per minute. Enter the drug continuously during the day. Replenishing magnesium deficiency in the body of a pregnant woman will prevent subsequent seizures.
With the introduction of a solution at a rate of 22 drops per minute, 2 g of dry matter will enter the woman's body every hour. Simultaneously with the administration of the drug, it is necessary to monitor whether symptoms of an overdose of magnesium occur, which include the following manifestations:
- half-breathing (less than 16 breaths per minute);
- inhibition of reflexes;
- reduction of daily urine output to 30 ml per hour.
In case of an overdose of magnesium-containing drugs, stop their use and in the near future introduce an antidote to the pregnant woman - 10 ml of calcium gluconate at 10% concentration. Anticonvulsant treatment is carried out infor the remainder of the pregnancy as long as there is a risk of eclampsia.
If, after the administration of magnesia, convulsions recur, the patient is given another, stronger drug - most often Diazepam. On average, 10 mg of the drug is injected into the body over two minutes. With the resumption of convulsive seizures, the drug is repeated at the same dosage. If convulsions do not recur within the next 15-20 minutes, supportive therapy is started: 500 ml of saline is used for 40 mg of Diazepam. The drugs are administered over 6-8 hours.
Lower blood pressure
Another important area in the provision of emergency care for eclampsia and preeclampsia is the antihypertensive drug effect. Scientists were able to prove that the use of other medicines does not play a significant role in stabilizing the condition of a woman and the development of the fetus. Neither antioxidants nor diuretics can help with this syndrome in pregnant women. Such treatment will not bring any benefit. Eclampsia and preeclampsia are treated only symptomatically, that is, with the use of anticonvulsants and antihypertensives.

In obstetrics, preeclampsia and eclampsia are direct indications for antihypertensive therapy, the purpose of which is to lower blood pressure to within 140/90 mm Hg. Art. and preventing its subsequent increase. For pregnant women suffering from the syndrome of multiple organ failure on the background of hypertension, such drugs are usedfunds like Nifedipine, Sodium Nitroprusside, Dopegit.
The maximum daily dose of drugs is calculated by the attending obstetrician-gynecologist individually for each patient, depending on the weight, severity of the disease. Some of the drugs are available in tablet form, while others are injectable. In the first days of treatment, specialists prescribe medications in the minimum dosage, gradually increasing the daily amount of active substances. Any changes in therapeutic tactics should be reflected in the treatment protocol. Preeclampsia and eclampsia in pregnant women require long-term maintenance antihypertensive therapy (taking drugs based on methyldopa) until childbirth. In the event of a sudden deterioration in the condition caused by a pressure surge, such remedies as Nifedipine, Naniprus and their analogues are recommended for urgent use.
It is impossible to complete magnesium and antihypertensive treatment immediately after childbirth. The woman in labor is prescribed the minimum dosage of drugs over the next day, which is especially important to maintain her blood pressure. As soon as the new mother's condition stabilizes, the drugs are gradually withdrawn.
Rules of delivery
The indicated clinical recommendations for eclampsia and preeclampsia are not always effective. In severe cases, the only way to cure this pathological condition is to get rid of the fetus, since it is pregnancy and the processes associated with the formation and nutrition of the placenta that cause the syndrome. If anticonvulsant andantihypertensive symptomatic treatment does not give the desired results, the woman is being prepared for emergency childbirth, otherwise no specialist can guarantee the safety of her life.
It is important to understand that eclampsia or preeclampsia itself cannot be called a direct indication for urgent delivery. Before proceeding with the stimulation of labor, it is necessary to achieve the cessation of convulsive seizures and stabilize the condition of the pregnant woman. Extraction of a child from the womb can be carried out both through a caesarean section and through the natural birth canal.
The date of delivery in case of multiple organ failure syndrome is prescribed by the doctor based on the severity and severity of the pathology. With mild preeclampsia, a woman has every chance of carrying a child to the due date. If a woman is diagnosed with a severe form of pathology, then childbirth is carried out within 12 hours after the relief of convulsive seizures.

Neither eclampsia nor preeclampsia are considered absolute indications for caesarean section. Even with a severe form of pathology, natural childbirth is more preferable. About cesarean section, we are talking only in complicated cases - for example, with placental abruption or ineffective labor stimulation. Induction, that is, labor induction, can also be considered a type of indirect medical care for eclampsia and preeclampsia. Pregnant women must use epidural anesthesia, control the heartbeat of the fetus throughout the process.
Thanthreatens multiple organ failure syndrome
An attack of eclampsia can provoke unexpected complications. In the absence of antihypertensive and anticonvulsant treatment, the pregnant woman is threatened by:
- pulmonary edema;
- aspiration pneumonia;
- development of acute heart failure;
- impaired cerebral circulation (hemorrhagic stroke followed by paralysis of one or both sides);
- retinal detachment;
- cerebral edema;
- coma;
- fatal.
Short-term loss of vision is not ruled out. In the postpartum period, eclampsia or preeclampsia can leave its mark in the form of psychosis, the duration of which reaches an average of 2-12 weeks.
Can the problem be prevented
Treatment of eclampsia and preeclampsia in pregnant women, as already noted, is purely symptomatic. At the moment, it is impossible to predict exactly whether this syndrome will develop in a pregnant woman or not, therefore, most experts recommend taking during pregnancy as a preventive measure for these pathological conditions:
- aspirin (no more than 75-120 mg per day), up to 20-22 weeks;
- calcium preparations (calcium gluconate, calcium glycerophosphate).
These funds reduce the likelihood of developing eclampsia in pregnant women at risk. Meanwhile, small doses of aspirin are also recommended for patients who do not have the risk of developing pathology.
Wrong is the opinion that as effective preventive measureseclampsia protrude:
- s alt-free diet and minimal fluid intake;
- restriction in the diet of proteins and carbohydrates;
- taking iron-containing preparations, vitamin and mineral complexes with folic acid, magnesium, zinc.
Recommended:
Dyspepsia of pregnant women: causes, symptoms and treatment

Dyspepsia of pregnancy is a common digestive disorder. It is faced by many women during the period of gestation. Pathology is accompanied by many symptoms. Dyspepsia in expectant mothers can be both physiological and pathological in nature. A woman should know how to get rid of this condition, as well as consult a doctor in a timely manner to avoid serious consequences of the disease
Early preeclampsia in pregnant women: signs, symptoms and treatment

During pregnancy, the female body has to solve a huge number of non-standard tasks. The work of many organs and systems is rebuilt, from blood circulation to metabolism. Unfortunately, our body does not always cope with this successfully, so there are malfunctions in the body that are typical for pregnancy. One of the most common pathologies of pregnancy is preeclampsia. It can be early or late
Fashionable pregnant women. Dresses for pregnant women. Fashion for pregnant women

Pregnancy is the most beautiful, amazing state of a woman. During this period, she is especially attractive, radiant, beautiful and tender. Every expectant mother wants to look stunning. Let's talk about what's trendy and more
Preeclampsia in pregnant women: causes, symptoms, treatment, diet, prevention

Such a disease as gestosis can be considered a kind of side effect of pregnancy, it is observed in many women who are in an interesting position. And as practice shows, it is 30%. Fortunately, after the birth of a child, the pathology disappears
Pneumonia in pregnant women: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment features and advice from gynecologists

It is very important for women in an interesting position to approach their own he alth with special care. At the slightest manifestation of a cold, you should consult a doctor to avoid complications, such as pneumonia, the consequences of which can be very serious