2026 Author: Priscilla Miln | miln@babymagazinclub.com. Last modified: 2025-01-22 17:55:21
Dogs, like people, can get sick and injured. Due to mechanical damage or disruption of the body systems, an abscess may develop in dogs, which requires treatment. Timely detection and treatment of the disease will help to avoid complications, which means that the animal will suffer less.
The concept of an abscess
Abscess in dogs is an inflammatory process that occurs in the skin, which is accompanied by the formation and accumulation of purulent formations due to necrosis (decay) of tissues. Under the skin, a bag is formed with pus, particles of necrotic tissue and pathogenic microflora. Around the sac, the tissues become inflamed and the walls of the abscess begin to form, which consists of a surface layer formed by fibrous connective tissue and an inner, pyogenic layer of granulation tissue. If no action is taken, the bag will grow and disturb the animal. In addition to being painful, abscesses negatively affect the generalhe alth status of the pet.
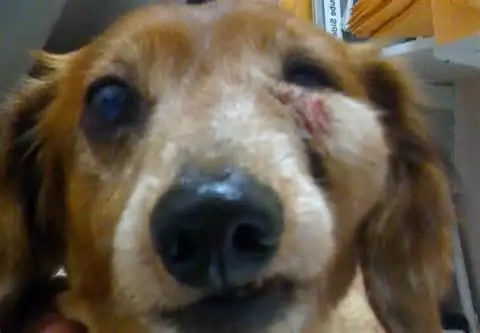
The disease can be localized on any part of the body due to mechanical damage: bruises, injuries and injections. And if there are malfunctions in the work of the secretory organs, then an abscess of the gland in the dog may develop.
When the paraanal gland becomes inflamed, the excretory canal is blocked, and the secret accumulates inside. Finding no way out, the liquid overflows the gland, and the wall and skin break. This is the abscess of the paraanal gland in a dog, which resembles an ulcer.
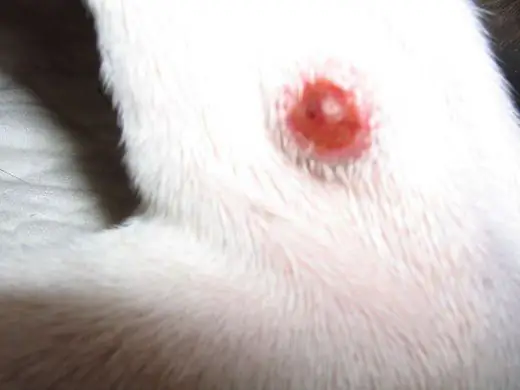
Causes of an abscess
The occurrence of an abscess is associated with the penetration of pathogens into the tissues through wounds and abrasions. Also, such a reaction can be provoked by toxic substances that have fallen under the skin. Often an abscess in dogs is formed when a purulent process begins in hematomas and lymphoextravasates, as well as when microorganisms are transferred by the blood flow from the focus of suppuration.
This disease is quite common among four-legged pets. According to statistics, every second dog suffers from an abscess, but the reasons for its occurrence are different:
- injections;
- abrasions, scratches, injuries, bruises;
- contamination of wounds;
- lack of hygiene procedures or lack thereof;
- germs and bacteria;
- wrong care.
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to determine the nature of the abscess and establish the degree and form of the disease.
Types and forms of abscesses
In veterinary medicinethere are several criteria by which it is customary to classify abscesses.
Morphological composition of purulent formations and provoking bacteria:
- benign;
- malignant.
Clinical manifestations:
- hot or spicy;
- cold or chronic.
Location of injury:
- superficial, which develops in the skin and subcutaneous tissues;
- deep, which can be subfascial, intermuscular, intramuscular, subperiosteal, bone, subperitoneal, abscess of organs and glands, depending on the location.
In a benign abscess, thick, creamy, purulent accumulations are formed, with an increased content of leukocytes, without microbes or with a small presence of them. A benign abscess can form if low-virulence staphylococci penetrate the tissues or when irritants are injected under the skin. Often such an abscess forms after an injection in a dog.

In a malignant abscess, purulent formations are watery and liquid, with a high concentration of pathogens and a low production of white blood cells. The causative agents of the malignant process are purulent-putrefactive and anaerobic microbes. Such an abscess in dogs is more painful and will not go away on its own. It can develop into a more complex form and affect adjacent tissues. Such formations require surgical intervention, in other words, they are removed through surgery.
For hot abscessthere is a pronounced inflammatory process, which is characterized by an acute course and the rapid formation of an abscess, which often opens spontaneously, that is, breaks through, and the pus flows out.
With a cold abscess, the main signs of inflammation are mild, and pus accumulates slowly, making timely diagnosis difficult. Such abscesses are characteristic of old and emaciated dogs that move little. An abscess is formed in the presence of low-virulence microorganisms.
How to recognize the disease
Abscess in a dog, the photo of which is presented in this article, can be determined visually if the symptoms are severe, but in some cases it is not without special examinations. With various inflammatory processes, the symptoms are different.
Symptoms of a benign abscess:
- swelling with clear edges;
- redness;
- pain when touched.
Symptomatic of malignancy:
- soft tubercle formation;
- increased animal body temperature;
- severe pain when pressed.

Abscess of the paraanal glands of a dog gives not only external symptoms, but also affects the general condition of the pet's body. Observed:
- sluggishness;
- sullenness;
- increased body temperature;
- lack of appetite;
- apathy and indifference to walks;
- anal passage area becomes inflamed;
- purulent ulcers form;
- tenderness of adjacent tissues is observed.
Do not try to clean the wound yourself, so as not to harm the animal. You should immediately contact a specialist.
If the symptoms do not indicate a specific type of abscess, and the pet's condition worsens, then you should immediately contact the veterinary clinic. Timely diagnosis and proper treatment will help to avoid complications.
Diagnostic Methods
Abscesses have much in common with hematomas, hernias and tumors, but the symptoms and contents of the formations are different. Therefore, in order to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment, the doctor conducts an examination and prescribes a series of examinations:
- the course of the disease is being studied;
- an abscess is examined and palpated;
- perform a puncture to examine the contents;
- compare the temperature of the affected area and he althy tissues.
If necessary, they can prescribe an MRI or ultrasound. This is especially true of internal formations.

How to treat the disease
Treatment of the disease is carried out by different methods. The veterinarian should prescribe a course of general and local therapy or recommend surgery.
If a benign abscess is diagnosed in a dog, treatment is carried out with medication, which consists of:
- absorbable ointments used to treat an unruptured formation;
- antiseptic solutions for treating wounds in case of spontaneous opening of an abscess;
- antiseptic ointments thatsuperimposed in the channels of wounds.
Rinse the affected area with a syringe so as not to cause unnecessary inconvenience to the pet.
When diagnosing a malignant abscess, an operation is prescribed to remove the purulent sac. Manipulation should be carried out as soon as possible, until the disease has spread to adjacent tissues. In the postoperative period, general and local therapy and a course of antibiotics are carried out.
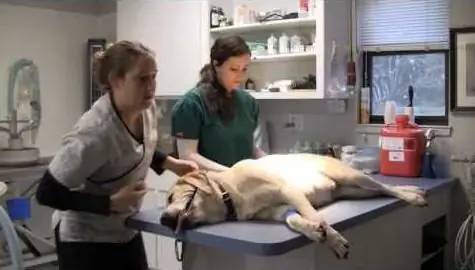
When the paraanal glands are affected, treatment should be carried out in a clinic. After examining and determining the extent of the problem, medication will be prescribed in combination with warm compresses. In more serious cases, the veterinarian opens and treats the abscess on his own. Often, additional drainage is required to remove pus. After that, treatment with strong antibiotics is prescribed to suppress the pathogenic microflora, using rectal suppositories and local treatments.
Prevention measures
By following a number of simple rules, you can protect your pet from disease and prevent the formation of purulent bumps. These include:
- observance of meticulous hygiene;
- regular inspections of the animal for damage;
- treating even minor wounds;
- providing proper animal care;
- regular vet checkups.
Abscesses should not be ignored to prevent complications. An abscess can form in a short time and grows rapidly, affecting anddestroying he althy tissues, as well as intensive multiplication of microbes that can infect the entire body of the animal.
Recommended:
Food for dogs of large and small breeds. Complete nutrition for dogs. Meat for dogs

In order for a beautiful he althy dog to grow out of a small puppy, you need to choose the right, well-balanced diet for him. After reading today's article, you will learn how to feed a shepherd dog and what to give a miniature lapdog
Diseases in dogs: symptoms and treatment, photo

The dog quickly becomes a member of the family, and everyone perceives its illness very close to heart. To notice the approaching danger in time, you need to be able to distinguish between the most common diseases and know their symptoms
Mastocytoma in dogs (mast cell tumor in dogs). What is this disease? Causes, treatment, prognosis
Various tumors and neoplasms, both malignant and benign, occur not only in humans, but also in pets. In addition, some types of diseases, such as mastocytomas, are more common in dogs than in humans. What is the treatment for this disease and what is it all about?
Cushing's syndrome in dogs: symptoms and treatment. Cushing's syndrome in dogs: how long do they live?

Today we want to talk about a serious endocrine disease that is common in dogs, and it is called Cushing's syndrome. How to recognize its symptoms, undergo the correct diagnosis and treatment? Answers to these and other questions in our article
Otitis in dogs: treatment with antibiotics and folk remedies. Types and symptoms of otitis media in dogs
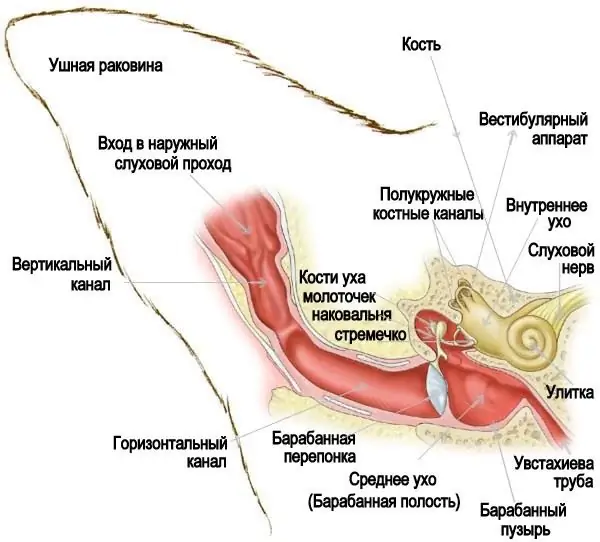
Otitis is an inflammation of the ear, which gives a lot of discomfort not only to people, but also to our smaller brothers. It is worth noting that animals are much more likely to suffer from such an ailment. If, after cleaning your pet's ears, you notice that the dog's ears are dirty again the next day, she constantly scratches them and shakes her head, and the secretion secreted smells unpleasant, then you should immediately visit a veterinarian

