2026 Author: Priscilla Miln | miln@babymagazinclub.com. Last modified: 2025-01-22 17:55:23
Otitis is an inflammation of the ear, which gives a lot of discomfort not only to people, but also to our smaller brothers. It is worth noting that animals are much more likely to suffer from such an ailment. Special glands, which are located in the external auditory canal, should normally secrete a small amount of secretion necessary to protect the ear canal from foreign substances, water, dirt and dust. For each breed of dog, the type and nature of the secretion of such a secret is individual.

If, after cleaning your pet's ears, you notice that the dog's ears are again dirty the next day, he constantly scratches them and shakes his head, and the excreted secret smells bad, you should immediately visit a veterinarian.
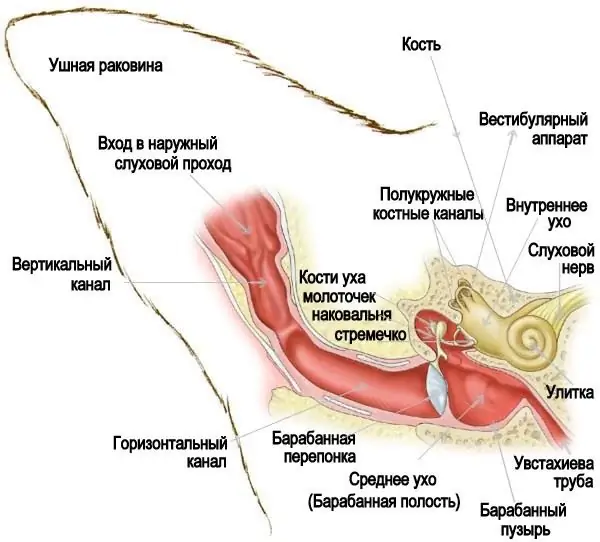
Otitis externa and otitis media in dogs
Depending on the localization of the pathological process, experts distinguish two types of disease:
- MediumOtitis media is characterized by inflammation of the middle ear, which is located behind the eardrum and consists of 3 bones that conduct sounds to the inner ear.
- Otitis externa is accompanied by inflammation of the external passage, located between the eardrum and the opening of this passage.
The severe stage of the disease can combine inflammation of both the external ear and the middle ear.
Primary and secondary otitis media
Like other pathologies, otitis has different causes. If the disease develops independently and self-sufficiently, then this is primary otitis media, and if it is a complication of some dermatological disease, then we are dealing with secondary otitis media. Let's dwell on this in more detail.
The secondary form occurs for the following reasons:
- dermatosis;
- atopy;
- thallium poisoning;
- ectoparasites;
- bad heredity;
- adrenal disease;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- thyroid problems.
It is worth noting that some breeds of dogs have a predisposition to develop otitis media. As a rule, it depends on the structural features of the auricle. The risk group can primarily include animals with hanging large ears, which do not allow air to flow freely, as a result of which favorable conditions are created for the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms. This situation is often seen in poodles and spaniels. But, for example, East European Shepherds suffer from the opposite problem: their overly open ears contribute togetting into the ear canal of various bacteria.

In chronic otitis externa, excess discharge, inflammation and swelling of the eardrum can be observed in the affected ear. The verrucous form of the disease is characterized by redness of the skin, the formation of warts, the appearance of pus and atypical sulfuric discharge.
Causes of otitis media
Such a disease occurs due to many factors. The disease can be provoked by head injuries, hypothermia, malnutrition, helminthiasis, allergies and decreased immunity.
The causative agents of otitis are streptococci and staphylococci, which are considered the most famous bacteria. They live in the dog's body all the time. However, they are activated and cause harm only under favorable conditions for this. Any failures in the protective system lead to the rapid reproduction of pathogenic microflora.
Manifestations of disease
Symptoms of Otitis in Dogs:
- redness of the ear canal;
- constant ear shaking;
- itch;
- soreness;
- unpleasantly smelling purulent discharge with blood impurities;
- increased temperature in the affected area;
- puffiness;
- increased lymph nodes on the affected side;
- oppression, lethargy;
- loss of appetite.

Consequences of the disease
Otitis media in dogs, which must be treated immediately, can lead to serious complications:
- chronic formdiseases;
- temporary or permanent hearing loss;
- discharge of pus through the eyes;
- feeding problems due to constant pain;
- strabismus.
To protect your pet from such problems, you should seek the help of a qualified veterinarian in time, who will prescribe competent treatment.
Diagnosis of disease
There can be many etiological factors that provoke ear inflammation. Treatment of otitis in dogs depends on the nature and nature of the disease. To quickly eliminate unpleasant symptoms, you need to carefully examine the animal and make a clear diagnosis, otherwise all subsequent measures will not give a positive result and may even worsen the condition of the four-legged patient.

Diagnostic steps:
- Visual inspection of the external passage is carried out by means of an otoscope - a device with illumination and lenses. The veterinarian examines the cavity of the middle and outer ear, assesses the condition of the skin and eardrum, determines the degree of swelling, examines the canal for the presence of mites, foxtail processes, and foreign bodies in it. For example, otitis media and otitis media in dogs is accompanied by external ear discharge, tenderness, redness, and swelling. In addition, the tympanic membrane begins to bulge in the canal area. Sometimes lymphadenopathy is found on the side of the lesion, which is accompanied by pharyngitis, tartar or gingivitis.
- Analyzingblood to establish the state of the animal's body and its allergic status. If there is a suspicion of hypothyroidism, a blood test is prescribed to determine the concentration of triiodothyronine and thyroxine in it. A positive result requires thyroid stimulation.
- Cytological examination of exudate allows you to determine the microflora, detect a tumor and induration of the sulfur gland, diagnose sensitivity to antibiotics and autoimmune diseases.
- Microscopy examines the composition and structure of skin samples and exudate secreted by the ear gland. The presence of parasites, pathogenic organisms and autoimmune diseases is determined.
- X-rays are taken if laboratory tests do not provide sufficient information. X-rays can detect polyps or tumors of the nasopharynx, which often provoke the development of chronic otitis media.
- Magnetic resonance and computed tomography are the most informative research methods. They allow assessing the state of the middle ear, detecting inflammation of the brain tissue and determining the degree of involvement of neighboring structures in the pathological process.

A veterinarian can prescribe an effective treatment for otitis media in dogs only after a comprehensive examination. Any form of the disease cannot go away on its own, so the launch of the pathological process and self-treatment can lead to serious complications. It is worth noting that in the secondary form of otitis media it is very difficult to identify the main cause of the development of the disease.
Treatment
Treatment of otitis media in dogs is complex. First of all, the symptoms are eliminated, and then the primary causes of the disease. It is very important to correctly combine anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics, such as Otoferanol, Normax, Otibiovin, Otipax, with local treatment agents, such as camphor oil, Amidel-gel, Amit and aversectin ointment in the presence of ticks, "Acaromectin", "Dekta". Treatment of otitis in dogs with antibiotics should be supported by immunomodulators such as Askorutin, Gamavit, etc. To relieve pain, the veterinarian may recommend Framycetin ear drops.

Treating at home
Treatment of otitis in dogs with folk remedies should be done carefully so as not to harm even more. First of all, you need to remove the extra secret. To do this, use a special lotion, liquid paraffin, saline or hydrogen peroxide. If the disease is advanced, and crusts have already formed from prolonged combing of the affected area, you can remove them with a cotton swab moistened with hydrogen peroxide. The remaining wounds should be smeared with brilliant green to prevent infection.
Suppurative otitis media in dogs requires immediate removal of the abnormal discharge. This can be done with boric alcohol. Such a disease is treated quickly if you turn to a specialist in time and start acting.

Disease prevention
First of all, you need to eliminate the factors thatcontribute to the development of otitis media. To do this, you should regularly carry out hygiene procedures and treat your pet's ears. Carefully monitor your dog's diet, which should contain the necessary fats, proteins, complex carbohydrates and vitamins. In addition, avoid stressful situations, which can also significantly reduce immunity.
Recommended:
Treatment of the common cold during pregnancy: safe medicines and folk remedies

In a pregnant woman, a runny nose can start unexpectedly and cause a lot of trouble. But even a common cold can have unpleasant consequences for the development of an unborn child
Cystitis during pregnancy: treatment with drugs and folk remedies

Treatment of cystitis during pregnancy must be done with caution. The disease affects expectant mothers regardless of the term and requires immediate treatment
Folk remedies for constipation in a child: treatment features, advice and recommendations from specialists

Constipation is a problem faced not only by adults, but also by children in various periods of life. This symptom occurs frequently in children. In this regard, parents are asking what folk remedies for constipation in a child can be used
Runny nose during pregnancy: treatment with medicines and folk remedies

Rhinitis during pregnancy worries almost all women. It is rare when it does not appear, since everything is mainly connected with the cardinal changes that occur in the female body. It is necessary to provide the child with the necessary "building material" and nutrients. Therefore, often the mother's immunity becomes vulnerable to various infections. But the common cold creates a favorable microflora for pathogenic microorganisms
Treatment of depression during pregnancy: drugs and folk remedies

Depression during pregnancy is the "acquisition" of our century. The hormones produced should supposedly bring more joy to a woman's life, and they are, but this is on condition that the pregnant woman is socially and emotionally protected. Strong stress and forcing negative attitudes for an emotionally unstable psyche at this time are completely contraindicated