2026 Author: Priscilla Miln | miln@babymagazinclub.com. Last modified: 2025-01-22 17:55:27
The cause of low blood protein during pregnancy is most often the woman's malnutrition, but this may also indicate serious diseases. However, during pregnancy, seemingly harmless "malnutrition" will lead to certain intrauterine pathologies in the development of the baby and cause complications during pregnancy and childbirth.
Total blood protein
Proteins are essential substances for life. It is the basic building block of all cells. They make up about 20% of the tissue mass. Proteins are the main component of all known enzymes. Most hormones are either proteins or polypeptides in nature. Some of the proteins are involved in the manifestations of allergies and immunity in general. Others are involved in the transport of oxygen, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, hormones in the blood,medicinal substances.
Total blood protein is the concentration of all proteins in the blood serum.
Physiological hypoproteinemia - low total protein in the blood, not associated with diseases, observed in young children, pregnant women, especially in the third trimester, while breastfeeding.
Indications for testing
Total blood protein is determined in each woman several times during pregnancy. This is done as part of a biochemical blood test. This blood composition test is carried out by:
- when registering a pregnant woman;
- 2nd trimester 24-28 weeks;
- in the third trimester at 32-36 weeks.

At the times listed, women are tested for blood without any deviations in their condition. The doctor will prescribe blood tests more often if the pregnant woman has he alth problems:
- tumors;
- liver and kidney disease;
- acute and chronic infections;
- systemic diseases.
Data on the dynamics of the total protein content in the blood help to assess the condition of the pregnant woman, to control the effectiveness of the treatment.
Carrying out the procedure
Blood for analysis is taken strictly on an empty stomach. It is better if at least 8 hours pass between eating and taking an analysis. Coffee, tea, juice are also food, you can only drink water.
Before the procedure, you can not physically strain (climbing stairs, gymnastics), emotional arousal is undesirable. Rest 10 minutes before taking bloodcalm down.
You can not donate blood after massage, physiotherapy.
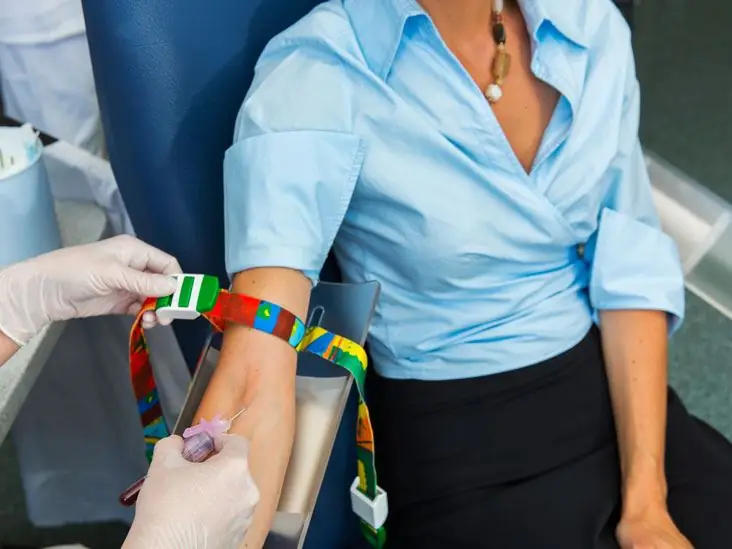
For blood sampling, a tourniquet is usually applied just above the elbow, in some laboratories this is not done. Blood is usually taken from a vein in the antecubital fossa.
Blood for determination of total protein is taken in test tubes with red caps. These tubes are needed to obtain serum. The total protein is determined, as well as other biochemical indicators, in biochemical analyzers. Usually a set of reagents is used to use the biuret method.
Mistakes in sampling can lead to a falsely elevated total protein level. For example, prolonged application of a tourniquet, physical activity, abrupt rising from a prone position.

Transcript
To express the content of total protein in the blood, mass concentration is used, showing the mass in 1 liter of blood (g / l). The amount of protein 60-80 g/l (6-8%) is considered normal. In pregnant women, the indicator is slightly lower - 55-65 g / l. The protein in the blood of a pregnant woman is especially noticeably lowered in the third trimester. The following norms have been adopted:
- first trimester - 62-76 g/l;
- second trimester - 57-69 g/l;
- third trimester - 56-67 g/l.
Only a qualified doctor should deal with the interpretation of a blood test. Even if a low protein content is detected, and the expectant mother feels well, she should still consult a doctor, there is no need to wait until signs of illness appear. Such an overlooked pathology will have time to harm the growing baby.
Reasonslow blood protein during pregnancy
In a he althy person, the protein content in the blood serum can fluctuate under the influence of various factors.
During pregnancy, the total protein in the blood is always lowered. This is due to an increase in blood volume, while the same amount of protein remains in the blood, thus a relative decrease in concentration is obtained.
Low protein in the blood during pregnancy can cause:
- insufficient supply;
- increased loss;
- violation of protein synthesis in the body.
It is also possible a combination of the above reasons.
Low blood protein in pregnant women is most often recorded when there is insufficient intake from food while following a vegetarian diet or starvation. Deficiency can be caused by a violation of the absorption of amino acids in the intestinal mucosa, for example, with inflammation or swelling in it.
Large protein losses occur in kidney disease (especially accompanied by nephrotic syndrome), blood loss, neoplasms.
Protein synthesis can be limited by a lack or lack of essential amino acids - building blocks that are not synthesized in the body, but come from food of animal origin - meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products. Synthesis disorders are possible with liver failure - cirrhosis, hepatitis, dystrophy.
The list of conditions accompanied by low blood protein during pregnancy indicates the non-specificity of this indicator. Therefore, the total protein content is not taken into accountfor the differential diagnosis of diseases, but for assessing the severity of the patient's condition and choosing a treatment.
Low Protein
Protein in the blood below normal during pregnancy is not a specific indicator. Therefore, the biochemical analysis of blood includes the determination of fractions - albumin and globulins.

Reduced albumin levels indicate malnutrition, malabsorption syndrome, acute or chronic liver failure, leukemia, tumors.
A decrease in the content of the globulin fraction is noted with malnutrition, congenital absence of gamma globulins, lymphocytic leukemia.
Informative is the determination of plasma fibrinogen. Its decrease occurs in cases of pregnancy with placental abruption, amniotic fluid embolism, may indicate meningococcal meningitis, leukemia, acute or chronic liver failure.

The biological role of proteins during pregnancy
During pregnancy, proteins provide:
- The growth and development of the baby, as well as the placenta and mammary glands, since proteins are the main building material.
- Transport of many nutrients, micro- and macronutrients, vitamins, since it is proteins that carry these substances in the blood.
- Child's innate immunity because antibodies are proteins.
- The balance of the coagulation and anticoagulation systems, since the substances that provide blood clotting (which will be extremely important to preventbleeding during childbirth) are proteins.
- Normal osmotic pressure of blood plasma because proteins attract water. When there are enough of them in the blood, the fluid is attracted to the vascular bed and does not accumulate in the tissues, which prevents blood clotting and edema.
Possible consequences of protein deficiency during pregnancy
Reduced protein in the blood during pregnancy is often due to malnutrition. According to studies, if a woman does not get enough protein from food, then due to the wrong diet, she also does not get enough calcium, magnesium, iron, vitamins, albumin.
Lack of protein in the diet is one of the causes of perinatal morbidity and fetal mortality. One of the most common syndromes of the perinatal period is intrauterine growth retardation, which complicates the course of many diseases.
The lack of vitamins seriously harms the he alth of the child, reduces resistance to infections, leads to prematurity, congenital deformities, the birth of weakened children.
Women with low blood protein during pregnancy reduce lactation to 3.5 months. The child has to be transferred to artificial nutrition.
According to studies, all women with low total blood protein during pregnancy had various complications of its course:
- iron deficiency anemia (76%);
- chronic placental insufficiency (63%);
- late gestosis (33%);
- threatened miscarriage (27%);
- fetal growth retardation syndrome (16%).
Pregnant women with a lack of protein in the diet also have complications during childbirth:
- ruptures of the birth canal;
- early rupture of amniotic fluid;
- weak labor activity.
The average weight of babies born to mothers with low blood protein during pregnancy is approximately 2900g
Normalization of nutrition and restoration of protein levels in the blood through nutritional correction significantly reduces the risk of pregnancy complications (anemia, fetoplacental insufficiency, late gestosis, developmental delay syndrome), as well as neonatal asphyxia.
Recommendations for normalizing indicators
First of all, women with low blood protein during pregnancy should normalize their diet - bring the ratio of BJU in line, pay special attention to the amount of protein foods, vegetable fats, vegetable foods. It is necessary to make a balanced diet, only it can fully satisfy the needs of the expectant mother.

Nutrition in the first half of pregnancy
During this period, the body of the expectant mother needs as many nutrients as before conception. In the first trimester, all the baby's organs are laid, so at this time it is extremely important to ensure that the body receives complete proteins, as well as vitamins, macro- and microelements in the correct ratio and quantity.
Depending on the weight, physical activity, nutritional status of a pregnant womanshould receive protein 60-90 g/day, fat 50-70 g/day. and carbohydrates 325-450 g / day. Calorie content of the diet - 2200-2700.
The diet should be complete and varied. Physiologically justified five meals a day. At nine o'clock in the evening - the last meal - a glass of kefir. Dinner should have no more than 20% of calories, and it is better to eat fatty and protein foods in the morning. Pregnant women should not rest lying down after eating.

Nutrition during the second half of pregnancy
In the second half of pregnancy, the expectant mother's nutritional needs increase due to the increase in the size of the baby, the beginning of the functioning of its organs - the kidneys, liver, intestines and nervous system. A woman needs 80-110 g of protein, 50-70 g of fat and 325-450 g of carbohydrates per day. That is, the need for protein increases, the amount of necessary fats and carbohydrates does not increase. Moreover, the protein must be at least 60% of animal origin. 30% of the protein should come from meat or fish proteins, 25% from milk and dairy products, 5% from eggs. The caloric content of the diet should increase to 2300-2800 kcal.
Diet to increase blood protein during pregnancy
Every day, the expectant mother should receive:
- meat and fish - 120-150 g;
- milk or kefir - 200 g;
- cottage cheese - 50 g;
- egg - 1 pc.;
- bread - 200 g;
- cereals and pasta - 50-60 g;
- potatoes and other vegetables - 500g;
- fruits and berries - 200-500 g.
It is necessary to consume foods containing complete proteins: milk, yogurt, kefir, mild cheese, low-fat cottage cheese. These products contain not only complete proteins, containing all the amino acids necessary for a person, but also calcium.

If the total protein in the blood of pregnant women is low, nutritionists recommend increasing the diet:
- meat and fish up to 180-220 g;
- cottage cheese up to 150 g;
- milk and kefir up to 500 g.
It is better to boil fish and meat, especially in the second half of pregnancy. It is necessary to abandon mushroom, meat and fish broths, gravy, as they contain a lot of extractive substances. It is better to cook vegetable or milk soups.
It is possible to increase the protein content in the diet with low blood protein during pregnancy through the use of nutritional mixtures that contain not only complete proteins, but also vitamins, unsaturated fatty acids, macro- and microelements.
Recommended:
Low blood pressure during pregnancy in the second trimester: causes, drug and alternative therapy

Low blood pressure during pregnancy in the second trimester is quite common. It is necessary to pay special attention to this. It is very important to control the pressure during the period of bearing a child, since a sharp decrease in it can have a negative impact on the course of pregnancy and the development of the fetus. The main symptom is dizziness, weakness
Monocytes are elevated during pregnancy: causes, rules for testing, consequences and prevention

When carrying a child, women are forced to constantly undergo a blood test, which helps to timely identify the presence of he alth problems and promptly eliminate them. It is especially important to take control of the situation in which monocytes are elevated in the blood. During pregnancy, making such a diagnosis after an examination raises a large number of questions in women - what kind of cells are they, what does their excessive number indicate, and what can this lead to?
Low blood pressure during pregnancy: what to do, what to take? How does low blood pressure affect pregnancy?

Every second mom has low blood pressure during pregnancy. What to do, we will analyze today. Most often this is due to hormonal changes. From the first days in the body of a woman, progesterone is produced. This causes a weakening of vascular tone and a decrease in blood pressure. That is, it is a physiologically determined phenomenon
How to lower blood pressure during pregnancy. Drugs that lower blood pressure during pregnancy

High or low blood pressure during pregnancy is unfortunately not uncommon. The difficulty is that during this crucial period you can not drink the usual medicines. You can increase or decrease the pressure during pregnancy with the help of folk remedies
Hypotension during pregnancy: possible causes, symptoms, treatment, normal pressure during pregnancy, advice and recommendations from a gynecologist
What is hypotension during pregnancy? Is it a simple ailment, or a severe pathology that requires immediate medical attention? That is what we will talk about today. During the period of bearing a baby, every woman is faced with various ailments, because the body works "in three shifts", and gets tired in order. At this time, chronic diseases are exacerbated, and "sleeping" ailments are awakened, which could not be suspected before pregnancy