2026 Author: Priscilla Miln | miln@babymagazinclub.com. Last modified: 2025-01-22 17:55:19
Even before visiting a pediatrician or a neurologist, it is useful for parents to know which reflexes in a newborn are normal. Of course, it is best to check them with an experienced doctor. But still, it does not hurt to understand how the child's nervous system works. Some actions that seem strange and even frightening to adults are actually a sign of normality.
Besides, the reflexes of newborns can not only be detected. They can still be stimulated, and this has a beneficial effect on the development of the nervous system. It is simply amazing what delayed consequences can sometimes be caused by stimulation of the physiological reflexes of a newborn. Of course, you don’t need to immediately aim to grow a child prodigy out of the child, ahead of their peers on all fronts. Such overwhelming parental ambitions will psychologically put pressure on the baby, and instead of long-awaited success, you can get neurosis or stuttering. But raising a he althy child is a worthy task. Interestingly, not all newborn reflexes go away in the first year of life. Some stay with us for life. Here is a small list.
Swallowing reflex
An adult, just like a baby, swallows food without hesitation. In a newborn, this happens when milk enters the mouth, and in us, when the food is chewed enough and has reached a semi-liquid state. Some people get used to eating hurriedly and chewing food poorly, but the reflex still works.
Corneal reflex
Otherwise, it is called "protective", and for good reason. This reflex is necessary to protect the eye. As soon as something touches the cornea of the eye, the eyelids quickly close. If not for this reflex, dust and fluff would constantly get into our eyes, we would accidentally grab the surface of the eye with our hands, which could not but affect our vision.
Tendon reflex
This reflex no longer seems to be as functional as the others, but it also lasts a lifetime. The traditional picture, already overgrown with jokes, is a neuropathologist hitting the patient with a hammer under the knee. What's happening? Muscle contraction.
Classification of reflexes
In general, the reflexes of newborns serve to adapt to the environment and are divided into the following groups:
- Reflexes that ensure the functioning of vital systems and organs - this includes the sucking and swallowing reflexes, reflexes of food and vestibular concentration.
- Protective reflexes - for example, the unconditioned reflexes of a newborn, which protect the eyes from touch and bright light. In this case, the baby squints.
- Orientation reflexes - turning the head towards the light source, search reflex.
- Atavistic reflexes - they fade over time. They areremind us of the previous links in evolution - the baby hangs, clinging like a monkey, swims like a fish.
In general, most of the unconditioned reflexes that are at birth fade away before the year. It has to do with brain maturation. The unconditioned reflexes of the newborn are controlled by deep and ancient brain structures, primarily the midbrain. Even in the womb, it matures faster than other structures in order to start working actively after birth. But after birth, the cerebral cortex develops rapidly and takes precedence over subcortical formations. On the basis of her work, conditioned reflexes of newborns are formed and gradually displace unconditioned reflexes, many of which have become unnecessary. And now it is worth listing them separately.
Sucking reflex
The baby was just born, barely recovering from the efforts that he, like his mother, showed during childbirth. He is in a completely new world in which he knows nothing. But as soon as he is applied to the breast, he begins to suck. How does he know what to do, and when did he learn to suck? And nature knows for it, because it is an unconditioned reflex. The sucking reflex in newborns is one of the most important because it provides nutrition. That is why he is so loved by pediatricians and neurologists.
How is it checked? You can’t breastfeed your baby every time you see a doctor or keep a bottle of milk? Checking the reflex is very simple. When you touch the lips or immerse your finger 1-2 cm into the mouth, the baby begins to rhythmically suck it. The reflex lasts up to a year,therefore, all doctors recommend continuing breastfeeding for up to a year if possible.

Search Kussmaul reflex
If you stroke the corner of the mouth, the baby will turn the head in the direction of stroking and lower the lip. It is worth pressing on the baby’s upper lip - he immediately raises both his lip and his head, and if on the lower one, the head leans down, and the lower lip goes down. In general, the child seems to follow the finger with his head and lips. This reflex exists up to 3-4 months. It is important that it be symmetrical. After all, the asymmetry of this reflex occurs when the facial nerve is damaged! The search reflex underlies many elements of facial expressions, such as nodding the head, smiling. And when feeding, you can notice that the baby does not immediately take the nipple, but shakes his head a little, as if trying on him.
Proboscis reflex
To check it, you need to sharply touch the nasolabial fold. The child immediately stretches his lips with a tube and turns his head, as if trying to find the nipple. This reflex also serves to nourish the baby. It fades by 3-4 months. A delay in its extinction may indicate a pathology of the central nervous system.
Palmo-oral reflex (Babkin reflex)
Pressing on the surface of the palm causes the mouth to open and the head to bend. It is normally present in all newborns and is especially noticeable before feeding. The absence of a reflex in a newborn or his lethargy is a warning sign, since it may indicate damage to the nervous system. It is most pronounced in the first 2 months, by the third it begins to fade. If athe child is older, and the reflex is preserved, this indicates damage to the central nervous system. In this case, the reflex may increase, and a light touch on the palm of your hand becomes enough.
Breath-holding reflex
Otherwise it is called the duck reflex. Helps the baby to be born without choking on amniotic fluid. May help in learning to swim. True, the cessation of breathing lasts only 5-6 seconds. With proper training, you can bring it up to half a minute. But it is better to be careful and contact a specialist who can teach a child to swim. Holding your breath longer than the prescribed time is harmful and dangerous.
Swimming reflex
When a child is immersed in water, he begins to move his arms and legs more actively. Babies also have such movements in their sleep, but in the water they intensify and become more frequent. Thanks to them, the child can hold out for some time on the water. But these movements are completely uncoordinated. If the swimming reflex is stimulated, children grow up he althier and calmer, and they also experience the pleasure of water. In the future, such people at any age will learn to swim more easily. Although the movements in any style of swimming are not at all like the floundering of a baby and are complex and coordinated. By the way, you can learn to swim from the age of 2, 5-3. And then it will no longer be a manifestation of an unconditioned reflex, but a motor skill.

Grasping reflex
If you run your finger along the baby's palm or stick your finger into his fist from the side of the little finger, the child will tightly clench his fist. Immediately, the tone of the whole arm increases -shoulder, forearm, hand, besides the skeletal muscles of the whole body. If you pick up the child, he may even hang, holding on to the index fingers of an adult. Small arms support the weight of the whole body!
The same thing can be observed if you give a child a toy, and then try to take it away. He clings to her tightly. "My!" - as if the reflex says. In fact, it serves as an attachment to the mother. There is a grasping reflex in newborns. It is especially strong in the first two months of life, in the third it begins to weaken, and by 6 months it goes away. But such a picture is observed if it is not developed.
If some reflexes after 2-3 months become a bad sign and all doctors and parents hope for their speedy disappearance, then the stimulation of this reflex helps to accelerate the development of the child. And yet after 4-5 months it should disappear. If it exists longer, this indicates damage to the nervous system. One of the best sports complexes for babies was invented, oddly enough, not by a doctor, but by an engineer. His name was Vladimir Skripalev. It all started with the fact that he created a sports complex for his own children. So, he just relied on the grasping reflex.

Plantar reflex (Babinski reflex)
Our body remembers the monkey past, when the legs looked like hands. Therefore, there is a semblance of a grasping reflex on the legs. This is the Babinski reflex. In response to the stroke stimulation of the sole, the foot bends and the toes diverge. The thumb is usually straightened, while the rest are bent. Also as withgrasping reflex, the overall tone of the legs increases, they bend at the knees.
Crawling reflex (Bauer reflex)
If you put the baby on his stomach and bring your palm to his legs, he will push forward towards them, as if crawling. It is useful to stimulate this reflex - it will strengthen the muscles of the body and help the baby to confidently hold the head on the 2-3rd week. It fades by 3-4 months. This reflex is absent or weak in children who have experienced birth asphyxia, trauma to the brain or spinal cord. When the nervous system is damaged, the reflex does not disappear for a long time, from six months to a year.
Stop reflex
To trigger this reflex in a newborn baby, you need to press the baby to your chest and lightly clap your palm on his soles. The child stretches and strains all the muscles. Stimulation of this reflex helps to develop muscles and even serves as a prevention of postural disorders. Such an exercise can also be carried out after feeding in order to free the baby's stomach from the air that has fallen during sucking. This is popularly called "keep up".
Heel reflex (Arshavsky reflex)
Pressing on the heel bone causes the extension of the entire body. This is accompanied by a disgruntled grimace and a cry. Such a reflex is observed only in physiologically mature children.
Step reflex
You need to hold the child above the table or any other horizontal surface so that he can touch it with one foot. When the leg rests on the table, it is immediately pressed in, while the other is pulled out. So the baby moves his legs, as if walking. No stimulation reflexfades away by 2-3 months. It is useful to stimulate it, because it affects the development of the child in many ways. Such children not only learn to walk earlier, but also have an early development of speech, and in the future they can boast of an ear for music and an ability for languages. Amazing connection, right? But that's how the unpredictable brain of a child works.
However, these "magic" actions can only be performed with children without orthopedic abnormalities. For any problems with the legs - clubfoot, hip dysplasia - it is harmful and dangerous to cause a step reflex and a stop reflex.

Fright reflex (Moro reflex)
The Moro reflex in newborns is triggered in response to a frightening situation. Therefore, there are several safe, but effective ways to check it. You need to take the child in your arms and lower it sharply by 20 cm, then raise it just as sharply. A baby lying on his back should sharply straighten his legs. You need to hit the table near the child's head with your hand. In all these cases, the baby is frightened, and then the Moro reflex is triggered in the newborn. The kid usually leans back, spreads his arms to the sides and opens his fists, and then abruptly returns back. This happens within a second.

Galant Reflex
When a child runs a finger along the back along the spine, he bends in an arc. The leg on the side of the irritant can also unbend. The reflex does not appear immediately after birth, but in 5-6 days of life.

Reflexes of maintenancecorrect posture or defensive reflexes
If many of the reflexes seem incomprehensible, mysterious and even unnecessary to us, then this set of reflexes is simply necessary for the survival of the baby. For example, what happens if you put a baby face down on his tummy? He will raise his head slightly (as far as he can) and turn it to the side. So he saves himself from suffocation. If the baby is lying on his back, and a diaper is put on his face, he will also not lie in the same position and breathe through the fabric. The baby will grab the diaper with his mouth, begin to turn his head, wave his arms and eventually throw off the diaper from his face. When the nervous system is damaged, the reflex is absent.
What does this mean? If you put such a baby face down, he may suffocate if you do not turn his head in time. With cerebral palsy, the picture is different. If the extensor tone is increased, then the child does not just raise his head, but arches back strongly.
Gag Reflex
The baby pushes out of the mouth all solid objects that fall there. The reflex will last for life, but the tongue takes part in it only for the first six months. By the way, this is one of the reasons why complementary foods during breastfeeding do not begin earlier. After all, the child will react with this reflex to a spoon and food and push everything out of his mouth.
Fencer's reflex
It is named after the appearance of the posture taken by the baby. The baby lies on its back, its head is turned to the side. He puts his arm and leg in the same direction. To some of the doctors, this pose reminded the pose of a swordsman before an attack. Reflex plays doublerole - on the one hand, it stimulates development, on the other hand, it slows down. After all, this reflex helps the baby look at his pen and focus on the toy squeezed in it. At the same time, he does not allow the child to hold the toy directly in front of him. He succeeds in this already at 3-4 months, when the reflex disappears.

Withdrawal reflex
Of course, no one will intentionally hurt the baby. But sometimes it is necessary, for example, to take a blood test. It is taken from the heel. At this point, the baby will pull the leg away, and the other will try to push the adult away.
Recommended:
How to dilute formula for newborns: a list with names, powder dosing and step-by-step cooking instructions
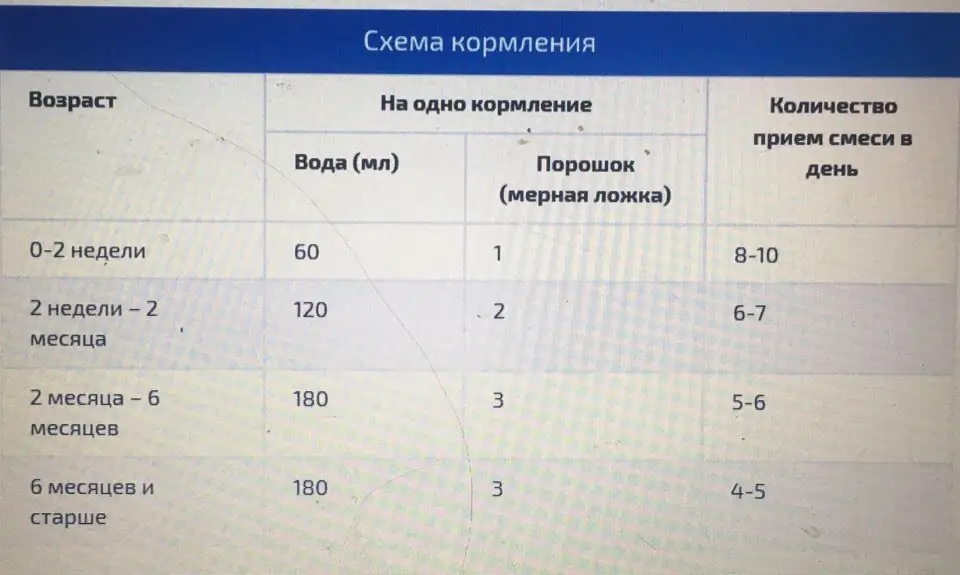
Probably everyone knows the benefits of breast milk for a newborn, but due to certain circumstances, not every woman can breastfeed her baby. For such cases, there are special mixtures, the manufacturers of which are trying to bring the composition of artificial nutrition substances closer to human milk. Any parent needs to know how to properly dilute the mixture for newborns, since the proportional ratio of dry matter and water directly affects the well-being and he alth of the baby
Organic cotton for newborns: description, properties and features

What is organic cotton? What benefits does it have and how is it used in the production of clothing and toys for newborns? Let's talk about eco-friendly things
List of essential items for newborns. Hygiene products for newborns

Your baby's birth is approaching, and you clutch your head in a panic that you still have nothing ready for his arrival? Walk into a children's store and your eyes widen in the widest range of children's accessories? Let's try together to make a list of necessary things for newborns
Pimples in newborns on the body: causes, diagnosis and treatment methods. Diaper dermatitis in newborns
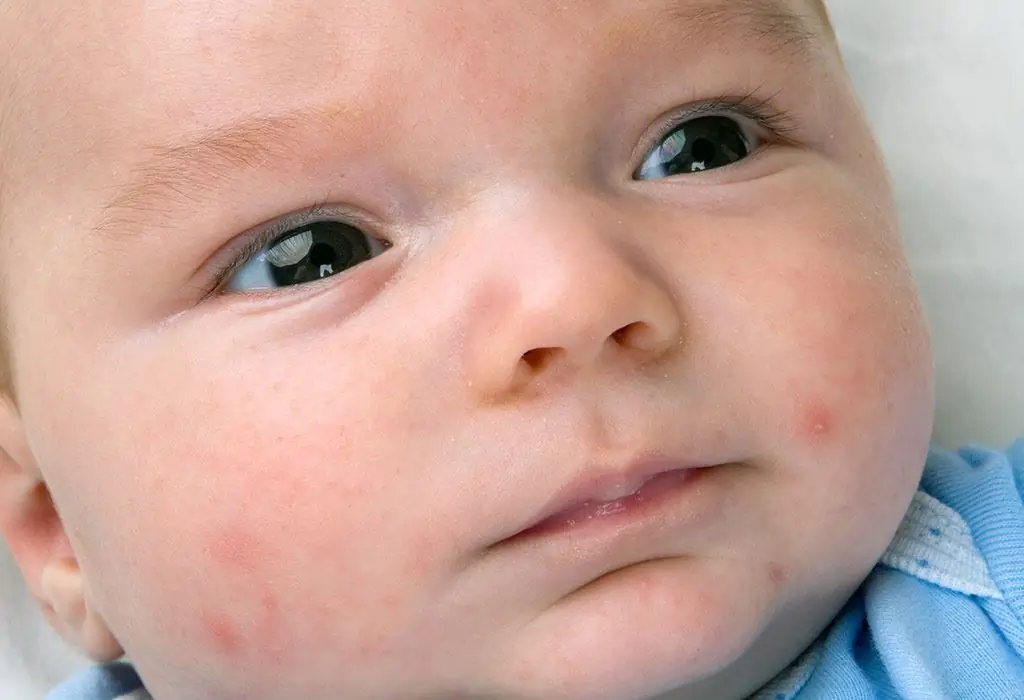
Pimples in newborns on the body are of particular concern to parents. They are red, white, single, large, small, etc. Moms are interested in the causes of pimples, as well as what to do in this situation. There are many known factors that cause acne. Some of them do not require any treatment, while others are an urgent signal to see a doctor
Different types of transport for children: list, description and features

Means of transport for children - a fascinating, interesting topic that introduces their classification, tells about the features and purpose of each variety. At the same time, the task of parents or teachers is not only to conduct a conversation, but also to consolidate the information received through various games

