2026 Author: Priscilla Miln | miln@babymagazinclub.com. Last modified: 2025-01-22 17:55:23
How can you tell if a child has an earache? Even children older than two years cannot always characterize the nature of the pain. What can we say about babies! Knowing the symptoms of otitis in a child, the disease can be "caught" at the onset phase.
If your ear hurts

With pain in the ears, the child becomes capricious, restless. Refuses to lie down, sometimes pulls at the ear. The shell or the area around the ear canal differs from the color of the skin of the cheek, looks inflamed. If the tragus - a knot located opposite the entrance to the ear - is lightly pressed, the baby will wince or whimper. All this points to the symptoms of otitis media in a child.
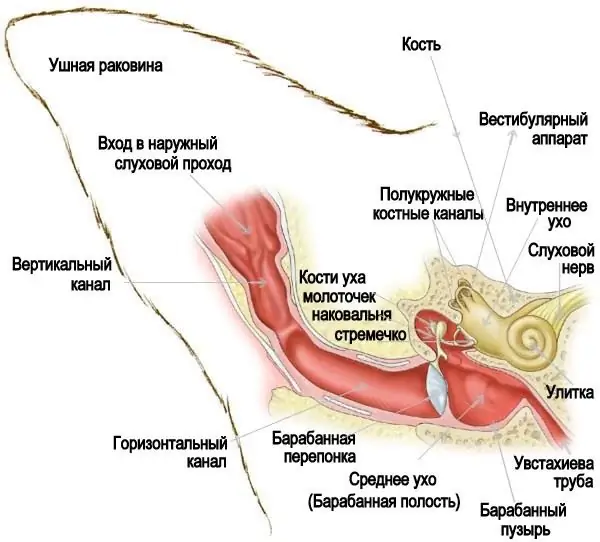
What is otitis media
Otitis media is an inflammatory disease of the ear. May have the form:
- external - inflammation develops in the ear canal;
- in the middle ear, behind the eardrum;
- internal - the disease affects the organs directly responsible for hearing: the cochlea and the labyrinth in which it is located.
The disease develops very quickly, passing from a subacute stage to an acute one. Otitis media is dangerous due to the development of complications, fromparesis of the facial nerve to hearing loss and meningitis and encephalitis. It occurs not only with colds or seasonal diseases - with any penetration of the infection into the ear canal or into the Eustachian tube, during caries, stomatitis, furunculosis.

With a runny nose and viral diseases, if the nose is blocked, otitis media instantly flares up in an infant. The symptoms of the disease are the same as in any other case. This is explained by the fact that in babies the Eustachian tube is located horizontally and wider, and with a runny nose, mucus easily flows into it.
Otitis media detected - parental actions
If symptoms of otitis media are found in a child, then it is necessary to consult a doctor. But it can't be done instantly! You can alleviate the condition of the baby by cleaning his nose and dripping it with vasoconstrictor drops. It is desirable to raise the baby to reduce tension in the eardrum. The pain syndrome is reduced if a folded flannelette diaper is applied to the ear or cotton wool is put into the ear passage so that the ear is warmed by its warmth. No vodka compresses or attempts to independently get into the ear canal with a cotton swab should be allowed! The infection can be brought deeper, and the catarrhal form of the disease will turn into purulent otitis media.
In a child, the symptoms of this disease can be seen by the outflow of pus from the ear. This happens when the eardrum is torn.
If this happens, the pain is relieved. But this does not mean that a doctor's consultation is no longer needed. Only an otolaryngologist should prescribe drugs depending onfrom the pathogen or cause that caused the disease.

Possible complications and precautions
Otitis media usually heals within 2 weeks and requires antibiotics. If you self-medicate and use remedies from the arsenal of traditional medicine without consulting a doctor, the infection can penetrate the eye socket or meninges.
In case of purulent otitis media, pus is constantly required to be removed from the ear canal with cotton turundas, with catarrhal it is possible to prescribe heating.
Together with the treatment of otitis media, it is necessary to deal with the elimination of the cause that caused it. If it is a catarrhal infection - gargle the baby's throat, if inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity - treat the mucous membrane with prescribed drugs.
When treating otitis media, care must be taken to ensure that the child does not have a stuffy nose and no additional pressure is created on the eardrum.
Similar symptoms of otitis in a child of any age and purpose are approximately the same. Only the doses of medicinal substances differ.
If in the treatment of otitis in infants and young children, parents are faced with such a difficulty as to prevent mucus from flowing into the child's ear - babies lie more, then with teenagers the problem is different. Explaining to an "almost adult" creature that no hair washing until the disease is over is sometimes more difficult than putting a baby with otitis media to bed.
Recommended:
Where are girls found? Where can you find a good girl? Where to find the girl of your dreams?

An article about the relationship between a man and a woman and where everyone can find a girl. The material also talks about what should be changed if you want to change something in your life, including in your personal life
The child does not want to communicate with children: causes, symptoms, character types, psychological comfort, consultations and advice from a child psychologist

All caring and loving parents will worry about the isolation of their baby. And not in vain. The fact that a child does not want to communicate with children can be a sign of a serious problem that will affect the formation of his personality and character in the future. Therefore, it is necessary to understand the reasons that force the baby to reject communication with peers
Where is love found these days?

Almost every person on the globe dreams of meeting his soul mate, his love. But, alas, not everyone succeeds. Often you have to go through various disappointments and very painful disappointments. What to do in order to fill as few bumps as possible on the way to that one or only one with whom happiness is possible? Where do other people find love?
Otitis in dogs: treatment with antibiotics and folk remedies. Types and symptoms of otitis media in dogs
Otitis is an inflammation of the ear, which gives a lot of discomfort not only to people, but also to our smaller brothers. It is worth noting that animals are much more likely to suffer from such an ailment. If, after cleaning your pet's ears, you notice that the dog's ears are dirty again the next day, she constantly scratches them and shakes her head, and the secretion secreted smells unpleasant, then you should immediately visit a veterinarian
Symptoms of teething in a child. How to help a child with teething
Teething starts at about 6-9 months of age. As a rule, these are the lower incisors. By 16-22 months it is time for the upper and lower canines. Most mothers know that teething these teeth is not easy. What are the symptoms of teething teeth in a child? How to lighten them?

