2026 Author: Priscilla Miln | miln@babymagazinclub.com. Last modified: 2025-01-22 17:55:24
What is placenta previa? This is a medical term that refers to various types of attachment of the placenta to the uterus. "Previa" indicates that the placenta is located (attached) close to the birth canal or even blocks them. Placenta previa during pregnancy is an anomaly, about its types and features of localization in the uterus of a pregnant woman and will be discussed in the article.
General terminology
The placenta is the connection between the baby and the mother, it is with the help of it that he receives oxygen and nutrition from her body, and it is through it that he gives up metabolic products.
The life of the child and how well the pregnancy develops directly depends on the state of this organ. That is why, when any pathology of pregnancy is diagnosed, a woman needs close medical supervision.
So, what is placenta previa? In obstetrics, it is considered- pathology or anomaly of pregnancy that develops:
- in the last weeks of pregnancy in about 0.4% of cases;
- at 20-33 weeks in 5-12% of cases.
As the baby grows and the uterus stretches, the placenta migrates, in this case, doctors note that the placenta previa has risen. That is, the organ took the place that nature intended.
To understand what placenta previa is, you should remember how the uterus works. This is a muscular organ that consists of the body, bottom and neck. The bottom is located at the top of the organ, the cervix is at the bottom of the uterus, and the body extends between them. The outer part of the cervix protrudes into the vagina.
During the birth process, the cervix opens under the pressure of the baby's head and his body passes from the uterus into the vagina. But the baby will not be born if the path is blocked by something. It is precisely such an obstacle that the placenta becomes, which occupies the space next to the cervix. It interferes with normal delivery, and this condition is regarded by doctors as a threat to the development and birth of the baby.
When placenta previa, the probability of death of a newborn is very high, it ranges from 6 to 25% of all cases. This level of mortality is due to premature birth, the wrong position of the child in the uterus. Placenta previa can cause severe bleeding in a woman and can be fatal. For example, about 3% of women die from bleeding. Due to child and maternal death, placenta previa is considered a serious and dangerous pathology.pregnancy.
Views
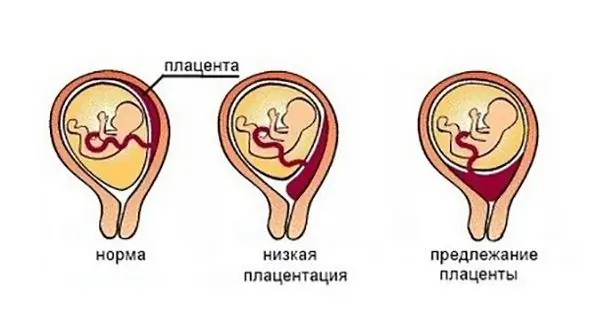
Depending on the localization of the placenta, there are several types of presentation. There are currently two classifications:
- The first is based on the location of the placenta during pregnancy using ultrasound.
- Second - on determining the location of the placenta during the birth process.
You should know that the type and degree of presentation change as the baby grows and the uterus grows.
According to ultrasound, there are such types of placenta previa during pregnancy:
- Complete - the placenta closes the entire intrauterine opening of the cervix. Even if the cervix is fully opened before childbirth, the baby will not be able to advance to the birth canal, as the placenta will interfere with it. Natural childbirth with such a pathology of the location of the placenta is impossible. The only way out in this situation is a caesarean section. It should be noted that this position of this organ in the uterine cavity is observed in 30% of cases of the total number of diagnosed presentations and is the most dangerous.
- Incomplete or partial placenta previa - the organ partially overlaps the cervix, leaving a small free area. With this position of the placenta during the birth process, the baby’s head, as a rule, cannot pass into a narrow gap. Therefore, the natural birth process in this case is also not possible.
- Low placenta previa during pregnancy is diagnosed when the placenta is attached at a distance of seven centimeters or less from the cervix. That is, the placenta does not overlap it. Against the background of low placenta previa during pregnancy, a natural birth process is quite possible. This is the most favorable type of pathology in terms of the development of complications.
A special case of low or incomplete is posterior placenta previa. In this position, it is attached to the back wall of the uterus.
Anterior placenta previa is another option for a low or incomplete placenta. In this position, it is attached to the anterior wall of the uterus. This arrangement is also called "placenta previa along the anterior wall." This position of the organ is not considered a pathology, but reflects a variant of normal localization. In most cases, posterior and anterior presentation are determined by ultrasound before 25-28 weeks of pregnancy, the organ can migrate within 10 weeks and take a normal position by the time labor begins.
This classification reflects the types of placenta previa during pregnancy as determined by ultrasound.
In addition to this typology, a clinical typology was used for a long time, which is based on determining the position of an organ during the birth process.
Based on the vaginal type of research during childbirth, the following types of position of the placenta are distinguished:
Central placenta previa
The cervix is completely blocked. With central placenta previa, a natural birth process is impossible. Relatively speaking, this is such an arrangement that is determined during the study before childbirth and corresponds to the full presentation established inresult of ultrasound during pregnancy.
Later presentation
During a vaginal examination, the doctor discovers part of the placenta that covers the cervix. This position during childbirth corresponds to an incomplete presentation, established as a result of ultrasound.
Posterior marginal placenta previa
The placenta is located near the cervix. Posterior marginal placenta previa corresponds to an incomplete presentation determined during pregnancy by ultrasound.
Reasons
Placenta previa is most often associated with pathological changes in the endometrium, which develop due to inflammation, surgery, complicated by previous births.
Uterine anomalies, endometriosis, multiple pregnancies, fibroids, cervical polyps can also be causes of placenta previa.
All these factors lead to the fact that the timely implantation of a fertilized egg in the upper segment of the uterus is disrupted, and it is attached in its lower part. Most often, placenta previa develops in women who give birth again.

Symptoms
The most important symptom of this pathology is bleeding, which is usually painless and recurrent. With placenta previa, bleeding can develop at any stage of pregnancy, but most often it occurs in the second trimester due to a strong and rapid increase in the uterus.
Bleeding causes placental abruption, that is, there is exposure of blood vessels,from which blood of bright red color follows.
Various factors can provoke bleeding: vaginal examination, strong physical activity, coughing, sexual intercourse, strong straining during bowel movements, visiting a sauna or bath.
Depending on the type of placenta previa, the following types of bleeding are distinguished:
- Profuse, sudden, painless, often occurs at night, characteristic of placenta previa. Such bleeding begins suddenly and can also suddenly stop, or it can continue for a long time in the form of scanty discharge.
- Bleeding in the last weeks before childbirth or during labor itself is typical for incomplete presentation.
Bleeding can be not only a symptom of pregnancy pathology, but also become its complication if it continues for a long time.
Pregnant women with prolonged bleeding may experience anemia, low blood pressure, fainting.
Indirect symptoms of placenta previa can be an incorrect presentation of the baby and a high uterine fundus.
Diagnosis

Diagnosis of pathology of pregnancy can be based on the characteristic complaints of a woman, on the results of an ultrasound or vaginal gynecological examination.
Characteristic signs of placenta previa are:
- Bloody bright red discharge with a relaxed and painless uterus.
- High fundus condition.
- Wronglocation of the baby in the uterus.
If a pregnant woman has these symptoms, the doctor will suspect placenta previa. In this case, a vaginal examination is not performed, as this can provoke profuse bleeding and the onset of preterm labor.
To confirm the preliminary analysis, the woman is sent for an ultrasound, which accurately determines whether there is a placenta previa and the degree of cervical overlap. Based on these data, the doctor makes a decision on treatment and chooses a method of delivery.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is the most harmless, harmless and informative method for diagnosing this pathology. This research method allows you to accurately determine the type of presentation, measure the area and thickness of the child's place (placenta), determine the areas of detachment, if any. To diagnose various characteristics of the placenta, ultrasound is performed with a moderately full bladder.
If pathology is detected, then ultrasound is performed every 2 weeks in order to determine the speed of migration. Doctors send a pregnant woman for diagnosis at 16, 24 and 36 weeks to determine the location of the placenta. If a pregnant woman has the opportunity and desire, then the examination can be done weekly.
Possible Complications
What threatens placenta previa? With this pathology of pregnancy, the following complications may develop:
- anemia;
- acute fetal oxygen deficiency;
- threatened miscarriage;
- preeclampsia;
- incorrect position of the baby in the uterine cavity;
- delayed child development.
The threat of termination of pregnancy occurs due to recurrent placental abruption, which leads to acute fetal oxygen deficiency and bleeding.
Anemia is caused by repetitive bleeding. Chronic blood loss develops, blood volume deficiency, its coagulability is disturbed, which can lead to the death of a pregnant woman in the birth process.
Incorrect position of the baby in the uterus, that is, its breech presentation is caused by the fact that there is no place in the lower part of the organ to accommodate the baby's head, since it is partially occupied by the placenta.
Intimacy and placenta previa
With such a pathology of pregnancy, intimacy is contraindicated, as this can provoke its detachment and bleeding. Any kind of excitation is contraindicated, as this can lead to intense contraction of the uterus, which is also unfavorable for placenta previa and can provoke not only detachment, bleeding, but also the onset of premature birth.
Treatment
Unfortunately, there is currently no specific treatment method that can change the location and attachment of the placenta in the uterine cavity.
Therefore, therapy for this pathology is aimed at stopping (stopping) bleeding and maintaining pregnancy, in the most ideal case, before the onset of labor.
When placenta previa, a pregnant woman must observe a regimen for the entire period, which is aimed atexclusion of causes that can cause bleeding. She needs to limit physical activity, not to have sex, not to jump, not to run, not to fly in an airplane, avoid stressful situations, not carry heavy things. From time to time you should lie on your back with your legs up. In this position, you need to rest whenever possible.

After 20 weeks with placenta previa, if bleeding is not heavy and stops on its own, a woman should undergo a course of conservative treatment, which is aimed at maintaining pregnancy until 38 weeks. Therapy includes the following medications:
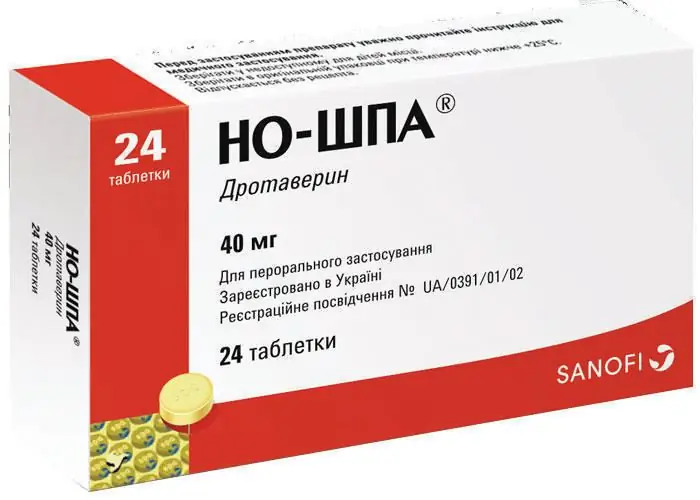
- Anspasmodics such as "No-Shpa", "Ginipral", "Papaverine", which improve the stretching of the lower part of the uterus.
- Iron medicines for the prevention and treatment of anemia, for example, Ferrum Lek, Totema, Sorbifer Durules, Tardiferon.
- Drugs to improve the blood supply to the fetus, for example, vitamin E, Trental, folic acid, Ascorutin, Curantil.
Often conservative treatment for mild bleeding consists of the following drugs: magnesia (intramuscularly), Magne B6, No-Shpa, Partusisten, Sorbifer, vitamin E, folic acid. The dosage and mode of administration is selected by the doctor individually for each woman.
These drugs will have to be taken throughout the entire period. If bleeding is profuse,urgently call an ambulance or get to the hospital on your own. In a hospital, a woman is injected intravenously with "Partusisten" and "No-Shpu", and in large doses, so that the muscles of the uterus are greatly relaxed and its lower section is well stretched. After that, the woman will again take medicines in the form of tablets.
For the treatment and prevention of oxygen starvation of the fetus, the following drugs are used:
- "Trental" (intravenously or in tablets);
- "Curantil";
- vitamin E;
- vitamin C;
- "Cocarboxylase";
- folic acid;
- "Actovegin";
- glucose - IV.
Therapy with these drugs is carried out in courses throughout pregnancy. If these funds allow you to extend the pregnancy up to 36 weeks, then the woman is hospitalized in the hospital and chooses how she will give birth: natural childbirth or caesarean section.
If severe bleeding develops in this pathology of pregnancy, which doctors cannot stop within a few hours, then an emergency caesarean section is performed to save the woman's life. In this situation, they do not think about the life and salvation of the fetus, since an attempt to maintain the pregnancy with severe bleeding will lead to the death of both the mother and the baby. An emergency caesarean delivery with placenta previa is performed for the following indications:
- Repetitive bleeding with severe blood loss.
- Regular bleeding with little blood loss, and the woman has low blood pressure and severe anemia.
- Simultaneous bleeding with severe blood loss (more than 250 ml).
- Heavy bleeding and complete placenta previa.
Birth

Childbirth with this pathology of pregnancy can be either natural or by caesarean section. The choice of the method of delivery is carried out by the doctor depending on the condition of the fetus and the pregnant woman, the type of placenta previa, the presence or absence of bleeding.
Caesarean section is currently performed in 70-80% of women with placenta previa. Indications for surgery are the following cases:
- Complete occlusion of the cervix by the placenta.
- Incomplete occlusion of the cervix, but combined with an incorrect position of the child in the uterus, as well as in the presence of scars and other injuries on the uterus, with multiple pregnancies, if the woman has a narrow pelvis, polyhydramnios, the age of the primiparous (over 30 years).
- Continuous bleeding, in which the volume of blood loss is more than 250 ml.
If the listed indications for surgery are absent, then the doctor will decide on the possibility of a natural birth.
Such births can be performed with placenta previa in such cases:
- No bleeding, or its complete stop, after the opening of the amniotic sac.
- The cervix has dilated enough and is ready for delivery.
- The contractions are regular and strong enough.
- Head (correct) presentation of the child.
With all this, doctors are waiting for the birth process to begin without the use of stimulant drugs. In the birth process, the fetal bladder is opened when the cervix is opened by 2 centimeters. If bleeding starts or does not stop after opening, an emergency caesarean section is performed. But in the absence of bleeding, childbirth is carried out in a natural way.
Prognosis for mother and child
With not heavy bleeding and timely surgery, the prognosis for the child and mother is favorable. Placenta previa is a life-threatening and he alth-threatening pathology, so you should undergo all the necessary examinations and strictly follow all the recommendations of your doctor.
When this pathology is detected in the first and second trimester, a pregnant woman should not be very worried, since the likelihood of "migration of the placenta" is very high and by the beginning of childbirth, she can take her natural, conceived by nature, position.
Placenta previa: reviews

Women who have carried a baby with placenta previa respond differently to this pathology. Most note that placenta previa was detected between 20 and 27 weeks of gestation and by the time of delivery, this pathology had resolved itself. That is, doctors call this phenomenon "migration of the placenta." For such women, childbirth and pregnancy proceeded safely, which they talk about on thematic forums.
Meet inInternet reviews of women whose placenta did not migrate by the time of birth, and they underwent a caesarean section. Their pregnancy was difficult, bleeding was regularly noted. Some went to the hospital to maintain the pregnancy. Women in such situations note that placenta previa is a very serious pathology.
In most cases, pregnancy with this pathology ended in the birth of a he althy and normal child, women on the forums talk about this, urging other pregnant women not to worry, not to worry and take care of themselves.
Prevention
A measure for the prevention of placenta previa is the prevention of abortion, the detection and treatment of genital pathologies, chronic inflammatory diseases of the genital organs.
At the stage of pregnancy planning, it is necessary to monitor the condition and change of the endometrium using ultrasound for 2-3 cycles.
During pregnancy, early diagnosis of anomalies is necessary, proper management of pregnancy, taking into account all risks and the likelihood of complications, choosing the method of optimal delivery.
A pregnant woman diagnosed with placenta previa should protect herself from emotional and physical stress. She must completely eliminate sudden movements, overwork, stress.
She should lead a proper lifestyle, get enough rest, be outdoors more often and be in complete emotional peace.
Rethink your diet to include iron-fortified foods. Constipation should be avoided.
Sowhat is placenta previa? This is a serious pathology in which the placenta was fixed in such a way that it partially or completely blocked the cervix. Such localization is an obstacle to the normal birth process, and also poses a threat to the he alth and life of the baby and mother.
But with the current level of development of medicine, most pregnancies with placenta previa are tolerated easily and end safely for both mother and child.
Recommended:
Hernia in a puppy: causes, symptoms, treatment, recovery period and advice from veterinarians
The occurrence of an umbilical hernia in a puppy is a fairly common pathology. With this defect, the internal organs (uterus, intestinal loop, omentum) fall out into the hole that has appeared in the lower abdomen. In most cases, the disease is hereditary
Hyperexcitability in infants: causes, symptoms, treatment, recovery period and advice from the best pediatricians

Hyperexcitability in infants is a fairly common problem today. The treatment process includes quite a lot of different elements that give results only when used together. The task of parents is not to miss the moment of healing
Cerebellar ataxia in cats: causes, symptoms, treatment, recovery period and advice from veterinarians

If a little kitten staggers when walking and falls, it always alarms the owner. The situation seems especially strange when there are no other he alth problems in the pet at the same time. The kitten has a good appetite, he is mobile and active, does not make a plaintive meow. But he is not able to walk normally, as a rule, from his very first steps. This may be a manifestation of cerebellar ataxia in cats
Vasomotor rhinitis of pregnant women: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, prescribed treatment, recovery period and advice from a gynecologist

Expecting a baby is a wonderful time in a woman's life. The expectant mother experiences the brightest emotions, but sometimes anxiety settles in her heart. A woman can worry about her well-being and the he alth of the unborn baby. Her anxiety is heightened if she exhibits symptoms of vasomotor rhinitis during pregnancy. You can cure a runny nose in a future mother with folk methods, but it is better to consult a doctor
Medical abortion in Minsk: medical centers, the best doctors, features of the procedure and the recovery period

Many ladies are looking for where to make a medical abortion in Minsk. This procedure is called pharmacological abortion and is more gentle than curettage. Today we will talk about where to do this procedure, which doctor to contact, about the features of medical abortion and about the recovery period

