2026 Author: Priscilla Miln | miln@babymagazinclub.com. Last modified: 2025-01-22 17:55:29
Cats and cats, just like people, are prone to the formation of sand and stones in the kidneys and bladder. This is urolithiasis (UCD), which causes pain, significantly impairs the quality of life of the pet. If certain symptoms appear, owners should contact their veterinarian. The faster they do this, the more likely the animal will get better. To recognize the disease, you need to know the symptoms of KSD in cats. This disease will be discussed further.
General characteristics of the disease
Many owners of four-legged pets are faced with the question of how to treat urolithiasis (MBD) in cats. What it is? Urolithiasis is also called urolithiasis. It affects cats and cats at different ages. This ailment is manifested by the accumulation of sand or stones in the bladder and kidneys. Previously, there was an opinion that sterilized animals suffer from thisdisease is much less common. However, recent research has dispelled this myth. A number of completely different factors influence the development of urolithiasis.

According to statistics, cats suffer from this disease 3.5 times more often than cats. This is due to the fact that they have a narrow and curved urethra, which is more quickly clogged with s alt crystals. It is also worth saying that ICD is diagnosed much more often in the Persian cat breed than in others. This is especially true for blue, cream and white animals. Also, urolithiasis is more often diagnosed in exotic longhair cats.
Considering the description of urolithiasis in cats and cats, it should be said that this is a systemic disease that is often chronic. It develops in the urinary tract of the animal. It is caused by the accumulation of s alt deposits in the form of sand and stones (urine stones) in the bladder and kidneys.
If not diagnosed in time, the disease can lead to the death of an animal aged one year or older. Therefore, owners should be aware of the symptoms of KSD. This will allow timely action to be taken.
Stones and sand can be different. In most cases, phosphate stones are found in animals. They are diagnosed at both young and old age. However, oxalate formations may also appear. Such stones are typical for cats and cats of advanced age.
Exogenous factors in the development of ICD
There are different causes of urolithiasis incats. The symptoms are almost always the same. A number of exogenous (external) factors can provoke the development of the disease. The first of these is crystallization. In the normal state, urine in cats and cats is slightly acidic. With an increase in the concentration of magnesium in it, as well as with an increase in the pH level above 6, 8, a crystallization process can occur. This situation occurs when eating certain foods, as well as the development of chronic urinary tract infections.

When urine is acidic, it prevents crystals from accumulating. It also has anti-infective properties. If there are many ions in the urine that take part in the formation of stones, even in an acidic environment, adverse processes can develop. Crystallization occurs when eating foods that contain large amounts of magnesium s alts. The same consequences are caused by urinary retention when the cat refuses to go to a dirty litter box, a sedentary lifestyle, insufficient water intake or its poor quality.
Considering the signs, symptoms and treatment of KSD in cats, there are a number of external factors that lead to sad consequences. In the diet, the amount of calcium should be more than phosphorus. You should also pay attention to the moisture content of the feed. If an animal consumes dry foods, while not having access to high-quality water, this leads to the development of KSD. Overfeeding and obesity are risk factors for developingailment.
Endogenous factors in the development of the disease
Urolithiasis (UCD) in cats can develop under the influence of endogenous (internal) factors. First of all, it may be hyperfunction of the parathyroid glands. Because of this, the amount of calcium in the blood and urine increases, specific stones appear in the kidneys and bladder.

When a bone is injured, the amount of calcium in the blood serum also increases. Such a complication can be observed with osteomyelitis, peripheral neuritis, osteoporosis. Chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract lead to the development of KSD. It could be gastritis, an ulcer, or colitis. Such diseases affect the acid-base balance in the body. Calcium s alts are also less excreted and bound from the small intestine.
Infectious diseases can lead to kidney and bladder stones and sand. The inflammatory process can be caused by various pathogens. They enter the body of the animal from the external environment, the genitals, as well as the urethra or intestines. It also affects the processes in the animal's body. As a result, a serious illness develops.
Cats have more concentrated urine than cats. Therefore, in certain conditions, the disease develops faster in them. With an excess of protein, s alty foods in the animal's diet, similar problems arise. Food quality should be high.
When considering the symptoms and treatment of KSD in cats, it should also be noted that in some casesthe cause of the disease is a lack of vitamin A in the diet. It strengthens the cells of the tissues of the urinary tract. Also, a hereditary predisposition leads to the accumulation of sand or stones. Hormonal imbalance and frequent overheating make urine concentrated. This also leads to the development of pathology.
Symptomatics
There are characteristic symptoms of urolithiasis. In cats, the disease manifests itself in a number of special conditions. It is worth considering that in the absence of blockage of the urinary tract, the pathology proceeds without obvious clinical signs. At this stage, laboratory tests are able to detect such diseases. Although there are no obvious signs of the disease, certain symptoms may occur. If the owner of the animal is attentive, he will be able to determine that something is wrong with the pet.

The cat's appetite decreases. This symptom should always alert the owner, suggesting that some kind of disease develops in the pet's body. S alt crystals may be deposited on the hairs near the urethra. If you look closely, you can see them. Also, the cat runs to the toilet more often than usual. This happens especially often after an outdoor game.
Also, the presence of discomfort may be indicated by the pet's kneading from foot to foot, raising and lowering the tail. The animal lies down carefully. This indicates the appearance of soreness.
How do kidney stones develop in cats? If the owner did not pay attention to the strange behavior of the pet in time,classic signs of ICD may appear over time. The cat has urinary colic. The act of urination is disturbed (the animal goes to the toilet anywhere). The composition of the urine may also change. It appears interspersed with blood, or it acquires a pinkish tint. The cat has anxiety attacks. He often adopts a position for urination, looks back at his stomach. The attack can last several hours. Between them, the cat behaves depressed, lies. If he rises, then very carefully, hunching his back.
Clogged duct
The symptoms of KSD in cats with blockage of the duct are quite specific. They are hard to miss. If this happens, it is important to contact your veterinarian as soon as possible. Otherwise, the animal will die. You need to see a doctor at the first signs of ICD. In this case, the treatment will require less time, and the pain in the animal will be minimized.

It should be understood that when the duct is blocked, the owners have literally a few hours to save their pet. When an attack occurs, breathing quickens, the animal's pulse rate increases. At the same time, the temperature rises quite rarely. Blockage of the urethra is called anuria. This is the most serious type of urolithiasis in cats. Only a veterinarian can make a diagnosis. At home, you cannot help the animal in this case.
When the pet is taken to the doctor, palpation of the bladder and kidney area will cause pain. Due to the inability to go totoilet in the upper urinary tract of the animal builds up pressure. The kidneys stop producing urine. At the same time, toxic substances that are formed during metabolism begin to accumulate in the blood.
This condition causes vomiting. The cat's belly becomes hard and large. This causes pain. If help is not provided, the animal falls into a coma and dies. Sometimes the bladder ruptures. This leads to peritonitis, the development of uremia. From the moment of blockage of the duct, a pet without proper medical care lives a maximum of 2-3 days. Therefore, measures must be taken very quickly.
Diagnosis
How to diagnose urolithiasis in cats? This procedure does not cause difficulties. Sometimes you can feel the stone if it's big enough. Most often it is detected with a catheter. When it is inserted, the device encounters an obstacle. This is the stone.

You can determine the presence of a stone in the kidney or bladder area by palpation of this area. This procedure causes pain. However, not only in such ways a veterinarian can examine his patient. A urine test is required. S alts, fresh erythrocytes, a small amount of protein are found in the biological material.
Based on the symptoms of KSD in cats, the doctor may also suspect complications in the course of this disease. This is confirmed by a urine test. When leukocytes appear in it, we can talk about the development of pyelonephritis.
Analysis allows you to determine the typecrystals in the urine. Based on this, the doctor prescribes treatment. The owners will not be able to independently restore the function of the urinary system in their pet. It is possible to make a mistake, which will lead to the most negative consequences.
Other diagnostic techniques
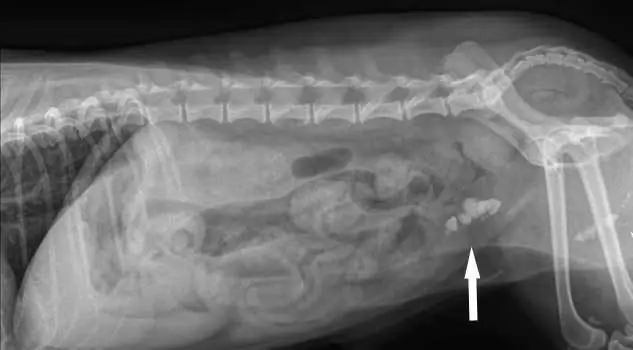
Treatment of urolithiasis in cats at home is possible only after visiting the veterinarian. He prescribes the correct treatment regimen. In addition to these types of diagnostics, X-ray examination can be used. This is one of the most modern methods that are used in the process of recognizing sand and stones in the body of a pet.

Most often, the veterinarian prescribes a survey urography. This survey reveals information about the size, location of the stones. Also in the pictures you can see their shape. Plain urography covers the entire area of the bladder, kidneys and ureter. It is worth considering that the shadow of the stones is not always visible on x-rays. This is due to their insufficient density for these rays. This situation occurs in 10% of cases.
An effective, informative method is the use of ultrasound. With it, the cat can determine the number, size and shape of stones. Also, with the help of this examination, you can determine the localization of stones. For ultrasound, stones are a denser substance than tissues. Therefore, such formations in the urinary system are clearly visible on ultrasound. Almost all types of stones can be seen with this type of examination.
Get the correct diagnosisit is not difficult for an animal in the presence of certain symptoms. However, at the initial stage of the disease, manifestations may be implicit. Therefore, the correct diagnosis is extremely important for the development of a treatment method.
Medicated treatment
Treatment can be operative or conservative. The second option is prescribed if the stones are relatively small, there is no blockage of the duct. The drugs used in the treatment of KSD in cats are aimed at relieving pain and inflammation. Treatment must be comprehensive. It is necessary to eliminate the factors that led to the development of pathology. The pet is on a special diet. This helps restore proper metabolism.
Medicines prescribed by the doctor eliminate the stagnation of urine. They also restore the normal patency of the urinary tract. If the animal has a spasm, special remedies can be prescribed that relieve it. Pain in this case is reduced. The sedatives and antispasmodics that are most often used in such cases include Atropine, Baralgin, Spasmolitin, etc.
At the clinic, the veterinarian can do a lumbar block with Novocaine. This relieves pain. Also, the animal is shown warm. Such actions stop colic. Diuresis is also restored. The condition of the animal is noticeably improving.
If there is an infection in the clinical picture, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. They are selected individually in accordance with the result of urine culture. flora must besensitive to the antibiotics prescribed by the doctor.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment of urolithiasis in cats and cats KSD is carried out in 20-25% of cases. This is necessary if there is a blockage of the duct or the stones cannot come out on their own. This procedure is necessary if the stones are quite large. Otherwise, infections will develop. Toxic substances will enter the blood of the animal. The operation leads to a positive result.
Prevention
Home treatment of urolithiasis in cats is possible only after consulting a veterinarian. He will prescribe the right diet. This will prevent similar problems from occurring in the future. In some cases, at home, the pet is given drugs that promote resorption and excretion of stones in combination with a special diet. These activities are assigned according to the type of stones.
Magnesium in feed should not be more than 0.1%. In this case, phosphorus in the composition should be less than 0.8%. Also regulate the weight of the animal. Cats must not weigh more than 3.5 kg and cats must not weigh more than 4.5 kg.
By examining the main symptoms of KSD in cats, you can quickly determine the development of pathology. The sooner the animal is examined by an experienced veterinarian, the less likely it is to develop negative consequences.
Recommended:
What are the diseases in cats: symptoms and treatment, photo

Animals, like people, can get sick. And not always an inexperienced owner can understand that it is time to take the pet to the doctor. Therefore, it is important to learn to identify the symptoms in advance in order to be able to help your pet at the right time. Consider in the article what diseases cats have, and what treatment is used
Scabies in cats: symptoms and treatment. Is scabies transmitted from cats to humans?

One of the common diseases of our furry pets is scabies. Scabies in cats is accompanied by itching, severe skin irritation, scratching and hair loss
Bleeding in cats: symptoms, sign of urolithiasis and treatment

Many owners believe that spotting in cats occurs due to pathologies of the urinary system. Indeed, a symptom may indicate inflammation processes or the formation of calculi. These diseases are often fatal. Therefore, if you feel unwell, it is important to take the animal to the veterinarian as soon as possible. Often, spotting in cats occurs due to an improper diet
Urolithiasis in dogs: symptoms and treatment

Our pets are not immune from various diseases. The problem is that they cannot openly tell what is bothering them, so an attentive owner can only suspect something is wrong by unusual symptoms. Urolithiasis in dogs is diagnosed quite often and requires timely treatment
Where do cats go after death: do cats have a soul, do animals go to heaven, opinions of priests and owners of cats

Throughout a person's life, a very important question is of concern - is there life after death and where does our immortal soul end up after the end of earthly existence? And what is the soul? Is it given only to people, or do our beloved pets also have this gift? From the point of view of an atheist, the soul is the personality of a person, his consciousness, experience, emotions. For believers, this is a thin thread that connects earthly life and eternity. But is it inherent in animals?