2026 Author: Priscilla Miln | miln@babymagazinclub.com. Last modified: 2025-01-22 17:55:27
Waiting for the birth of the desired baby is an amazing time in the life of both parents, mothers - especially. So far, she is not only the closest relative to her child, but the whole world and a cozy home. However, sometimes the mother's body regards the little man growing inside as an enemy and begins to behave accordingly. This situation is typical for Rh-conflict during pregnancy. It can happen only under certain conditions and is not a cause for panic, but awareness of the issue and timely knowledge that you are at risk will help to avoid serious consequences.
What is the blood Rh factor, how can it be positive or negative?
The blood of each person contains erythrocytes - red blood cells, not the same in all people. On the surface of erythrocytes is a complex of antigens - a certaina set of marker proteins by which human blood is classified - referred to one or another group. The more similar the complex of these proteins is in people, the greater the compatibility of their blood (the blood of one suits another when transfused, for example).

The Rh factor (otherwise Rh or simply Rh) is one of the antigens that is present in the erythrocytes of most people in the world. There are many antigens in total, but when determining the Rh factor, they talk about protein D. Europeans have it in 85% of cases, Asians in almost 99% and Africans in 93-95%. These people are called Rh-positive or have a positive blood type. The rest, respectively, will be the owners of negative blood.
This difference does not affect the functioning of the body and the general he alth of a person. The information is important in case of a blood transfusion or when planning a pregnancy if the expectant mother is Rh-negative.
How and when Rh is determined, the likelihood of conflict
A person's Rh factor is determined at the moment of conception and, except in rare cases, remains unchanged throughout life. The probability is determined genetically, depending on what RH each of the future parents has.

Sometimes there is a conflict in the blood group during pregnancy, and Rh in this case is absolutely nothing to do with it. Violations are caused by incompatibility according to the AB0 system (most likely, when a woman has the first group - 0, and a baby has any other one that contains enzymes in red blood cells,missing from the mother). However, this cause of the pathology is rarer than the Rh conflict (approximately one case in two to three hundred of all pregnancies, accompanied by risks of blood incompatibility).
A mother with a positive Rh blood factor has no reason to conflict with her unborn child, even if his Rh does not match hers, because in this case there is a protein in the female erythrocytes that the baby does not have. Therefore, for the mother's body, no component of the fetal blood will be alien, there will be nothing to protect against.
If mother and child are both Rh-negative, the immune system will not respond either, since protein D is absent in both.
Chance for a Rh-conflict in blood type during pregnancy is only for couples in which the mother is Rh-negative and the father is positive. In this case, having inherited the Rh blood from the father, the baby can become hostile to the mother's body on this basis. However, such a reaction of the female body does not always occur and not immediately. In numerous forums, you can find a lot of reviews about Rh-conflict pregnancies at risk, but in the end they are not problematic. Often Rh-negative mothers of two or more Rh-positive children have never encountered the problem of blood incompatibility.
The occurrence of Rhesus conflict

In the process of bearing a child, his blood and mother's blood mix. This can occur during natural childbirth, during a caesarean section, interruption of a normal or ectopic pregnancy, in cases of diagnosticprocedures when the study is carried out using samples taken from the body of an unborn baby.
If there is no D protein in the mother's blood and it never got into her, then her body has not yet developed antibodies to the foreign antigen. After such a case, the Rh-negative organism produces antibodies to get rid of the hostile element in the blood, but the first substances produced are not very strong and are not able to overcome the protective barrier of the placenta to harm the baby. Therefore, Rh conflict during the first pregnancy is unlikely.
However, when a Rh-negative mother comes into contact with a positive child again, her body already has the experience of protection and produces antibodies of a different class, stronger ones. They easily overcome the placental obstruction and enter the blood of the fetus, which can harm and cause negative consequences for the child.
Rh conflict in pregnancy becomes more possible and more intense with each successive contact of an Rh negative mother with positive blood, be it pregnancy or a wrong transfusion. Therefore, it is vital for women with Rh- to know about the characteristics of their blood. It is important to avoid abortions and unsuccessful pregnancies.
Symptoms of Rh conflict during pregnancy
There are no special manifestations of the Rhesus conflict that are noticeable to the expectant mother. This fact does not affect the feelings of a woman in any way. To determine pathological disorders, a laboratory study and ultrasound examination will be required.
Some experts note a general deterioration in the condition of the mother withthe occurrence of a Rh conflict in the blood group during pregnancy, the appearance of edema, an increase in blood pressure. This phenomenon is called the "mirror syndrome" - the more antibodies to the baby's blood the mother produces, the worse she feels. However, the results of such studies have not been scientifically confirmed, officially doctors do not link these two facts.
Manifestations and consequences of Rh-conflict during pregnancy directly affect the baby.

What threatens the Rh-conflict?
The occurrence of Rhesus conflict during pregnancy threatens the he alth, and sometimes the life of a little man. Exposure to maternal antibodies can lead to complications such as:
- miscarriage;
- birth of a premature baby;
- hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn.
All complications that arise as a consequence of the Rhesus conflict can be attributed to problems associated with hemolytic disease, but not in all cases, doctors can reliably determine the cause of premature voluntary termination of pregnancy.
How does hemolytic disease manifest?
Otherwise, this dangerous pathology is called fetal erythroblastosis. The main disorder in the body is the breakdown of red blood cells (hemolysis). Hemolysis products are toxic and cause edema, hemolytic jaundice (an increase in the amount of bilirubin pigment in the blood, one of the main components of bile resulting from the breakdown of red blood cells), hemolytic anemia (a decrease in the amount of bilirubin in the blood).erythrocytes and hemoglobin - the pigment of the blood responsible for the transport of oxygen).
Consequences of hemolytic disease
Intrauterine symptoms of hemolytic disease are fixed in the second half of pregnancy. Depending on the form of its manifestation, the possible complications are also different.
Anemia provokes a lack of oxygen and can lead to pathological changes in the central nervous system, including the brain, slower fetal growth, disorders in the functioning of the intestines, heart, kidneys. With a severe manifestation of the disease in a newborn, many problems can appear, both in the work of various body systems and in mental development. Usually this form of the disease is milder and the prognosis for the development of the child is often favorable.
Jaundice during pregnancy is almost not manifested, complications mainly concern already born children. In the first few days of life, intoxication of the body, a significant increase in the volume of the liver and spleen, manifestations characteristic of a severe form of the anemic variant of the disease, are detected. There may be convulsions, a heart attack, disorders in the respiratory system, leading to the death of the baby. Predictions are based on the degree of damage to the nervous system, ranging from normal child development to mental retardation or death.
Edematous manifestation of hemolytic disease is the most dangerous and severe. It is expressed in a strong general edema, the presence of fluid in the cavities of the child's body. The liver, heart, spleen are greatly enlarged. Often results in fetal or neonatal death.

Measures to eliminate hemolytic disease
It is not always possible to get rid of the consequences of the disease, but in cases where there is a chance of defeating the disease, the faster the treatment process begins, the higher the chances of saving the baby and its further normal development.
A newborn is given several blood transfusions - first, a general replacement, and then infusions aimed at regulating its individual necessary components. In severe prenatal manifestations of the disease, blood transfusion is carried out in utero.
Intravenous administration of special nutritional fortifying solutions or heavy drinking is prescribed.
Maternal breastfeeding is canceled for approximately three weeks - it is during this time that antibodies to the components of the baby's blood are excreted from the female body. During this period, mother's milk can be used, but only after boiling.
The consequences of the disease, which manifested themselves later - with the further development of the child - are corrected in accordance with their type and severity.
Prevention of hemolytic disease
Hemolytic disease prevention methods are:
- preventing a potential mother from producing Rh-positive antibodies: avoiding incorrect blood transfusions, avoiding abortions;
- elimination of the consequences of the primary manifestation of blood incompatibility after childbirth, ectopic or incomplete pregnancy. In these cases, a woman is injected with anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin - this isa kind of vaccination against the occurrence of Rhesus conflict during pregnancy. The injection is done once intramuscularly in the event that antibodies in the mother's body have not yet formed. This procedure is carried out at the 28th week of pregnancy and again within 3 days after the birth of a child with Rh-positive blood, or once after childbirth (many questions are asked about the reasonableness of such a vaccination on the forums, most experienced mothers are advised to resort to such a procedure only from the second Rh-conflict pregnancy); with a high probability of miscarriage or miscarriage that occurred at any gestation period; after abortion; when detecting possible damage to the tissues of the abdominal cavity - after some types of intrauterine diagnosis or injury.
Precautionary measures can reduce the possibility of developing an Rhesus conflict to a minimum. In some countries, this responsibility rests entirely with the attending physician, and if a Rh conflict is detected, the specialist loses his diploma.

Diagnosis of Rh factor conflict during pregnancy
Expectant mothers registering for pregnancy donate blood three times - at the first visit to the doctor, at the 30-week gestation period and immediately before childbirth. This schedule is standard and can be changed if more careful monitoring of the condition of mother and baby is necessary.
In the case of a woman with negative blood, an analysis for the Rh conflict during pregnancy is carried out at least once a month. Early diagnosisRh blood of the fetus allows you to take timely measures and avoid more traumatic and dangerous procedures.
Standard secondary ultrasound in any pregnancy between 18 and 24 weeks of gestation reveals primary signs of fetal hemolytic disease. Depending on the presence and course of the disease, further examinations are prescribed:
- If the blood test and ultrasound do not show the presence of abnormalities, then the third screening is carried out at the standard time (at 32-34 weeks of pregnancy).
- When determining antibodies to Rh-positive blood in the mother's blood, but there are no developmental disorders of the fetus, determined by the second ultrasound, the study is repeated every two weeks.
- In case of detection of signs of hemolytic disease on ultrasound examination, the fetal condition is monitored much more often - from daily to weekly. The frequency is determined by the indications of the current diagnostics.
Signs of Rhesus conflict during pregnancy, determined by ultrasound, are: an increase in the spleen and liver of the fetus, thickening of the placenta by more than 5 millimeters, excessive volume of amniotic fluid, expansion of the umbilical cord vein to a diameter of more than one centimeter. Additionally, the fetal blood flow velocity can be measured. If the blood in the middle artery of the brain moves too fast, invasive diagnostic procedures are prescribed - an analysis of biological material taken directly from the fetus or of fetal origin (amniotic fluid, placenta, cord blood).
Invasive procedures are carried out only in case of emergency and only with the consent of the mother, as they carry a certain risk for the unborn baby.
Childbirth with Rhesus conflict
Vaginal birth is considered preferable in pregnancies with Rh conflict, as surgery increases the risk of the mother's abundant Rh-positive blood entering the mother's body, as well as increasing the sensitivity of her immune system to D antigens.
Still, in some cases, caesarean section is preferred:
- severe fetal hemolytic disease;
- underdevelopment of the cervix or its immaturity before childbirth (physiological unpreparedness, unsoftened, which should normally occur 2-4 days before childbirth);
- extragenital pathology - any of the many different diseases of the body, disorders and syndromes of varying severity and significance, manifested in a pregnant woman and not associated with gynecological diseases or directly complications of the process of bearing a child.
Is it possible to have a successful pregnancy after a burdened one?

With all the possibilities of modern medicine, cases of unsuccessful completion of an Rh-conflict pregnancy are still recorded - fetal death, increased production of antibodies to positive Rh blood in the mother.
Even with such pathologies, one should not despair and give up the hope of giving birth to a he althy baby, since artificial,in vitro fertilization of an Rh-negative mother with a blood-compatible embryo.
Recommended:
Chlamydia during pregnancy: symptoms, treatment, consequences for the baby

What can darken the mood of a future mother in anticipation of the birth of a baby? Only possible pathologies like chlamydia during pregnancy. And this disease is considered especially dangerous for an unborn child. What threat comes from a disease that is transmitted from one person to another mainly through sexual contact?
Rubella during pregnancy: consequences for the fetus, symptoms and treatment
What is the common childhood rubella disease during pregnancy? How can this disease be recognized? What threatens rubella transferred during pregnancy? Consequences for mother and child. How to exclude the possibility of rubella during pregnancy? Do I need to be vaccinated against it? Are there complications in children after childbirth if the mother has had rubella during pregnancy?
Alloimmune antibodies. Rhesus conflict during pregnancy: consequences for the child

Alloimmune antibodies are formed in those women who have a conflict on the Rh factor. However, many women, having received the test results in their hands, do not always understand what consequences this can lead to
Rhesus conflict between mother and fetus during pregnancy: table. Immune conflict between mother and fetus
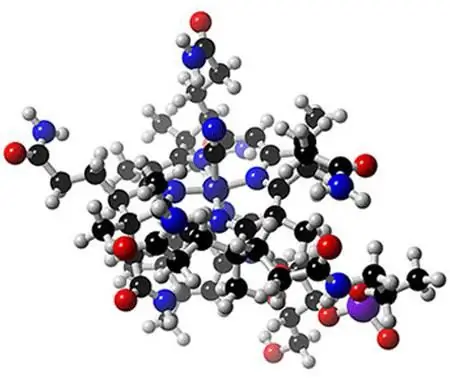
Rh-conflict between mother and fetus during pregnancy carries a great danger for the unborn child. Early diagnosis and careful planning of pregnancy will prevent serious consequences
Hypotension during pregnancy: possible causes, symptoms, treatment, normal pressure during pregnancy, advice and recommendations from a gynecologist
What is hypotension during pregnancy? Is it a simple ailment, or a severe pathology that requires immediate medical attention? That is what we will talk about today. During the period of bearing a baby, every woman is faced with various ailments, because the body works "in three shifts", and gets tired in order. At this time, chronic diseases are exacerbated, and "sleeping" ailments are awakened, which could not be suspected before pregnancy

